| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Piroxicam
CAS:36322-90-4 |
|
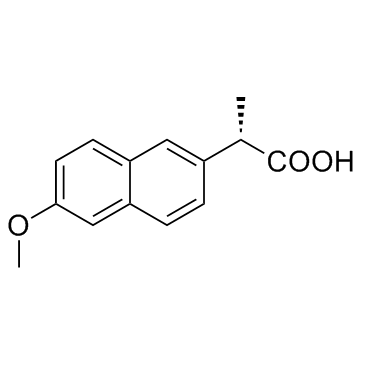 |
Naproxen
CAS:22204-53-1 |
|
 |
sodium dodecyl sulfate
CAS:151-21-3 |
|
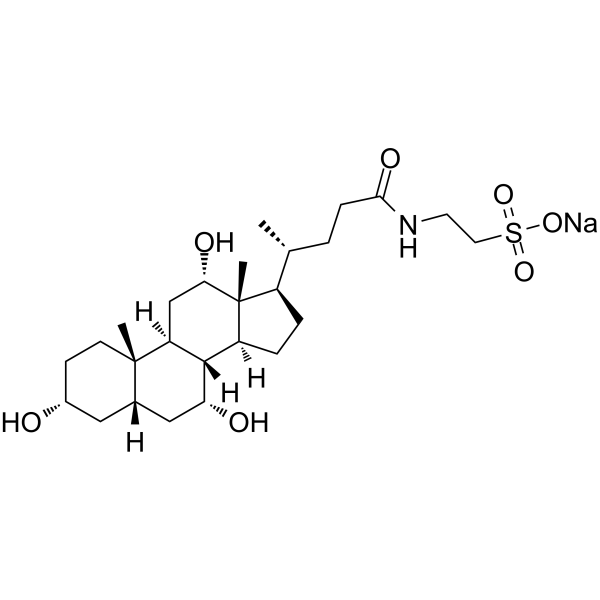 |
Sodium taurocholate
CAS:145-42-6 |
|
 |
L-(+)-Lysine monohydrochloride
CAS:657-27-2 |
|
 |
Furosemide
CAS:54-31-9 |
|
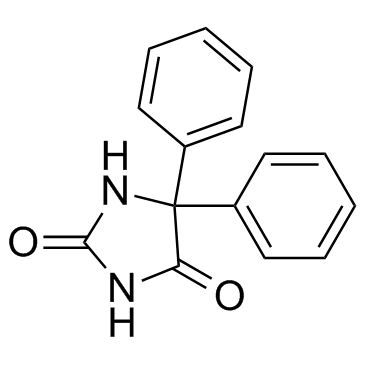 |
phenytoin
CAS:57-41-0 |
|
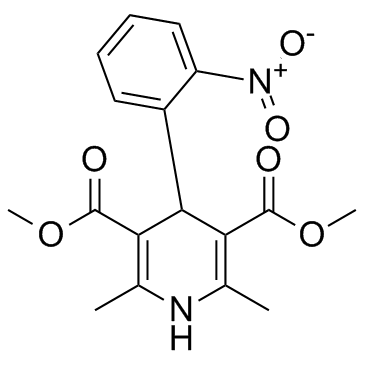 |
Nifedipine
CAS:21829-25-4 |
|
 |
Cilostazol
CAS:73963-72-1 |
|
 |
Danazol
CAS:17230-88-5 |