| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Sodium hydroxide
CAS:1310-73-2 |
|
 |
sucrose
CAS:57-50-1 |
|
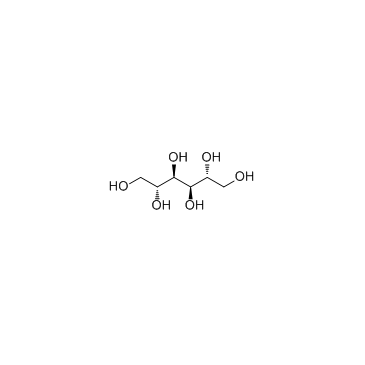 |
D-Mannitol
CAS:69-65-8 |
|
 |
3-Ethyl-2,4-pentanedione
CAS:1540-34-7 |
|
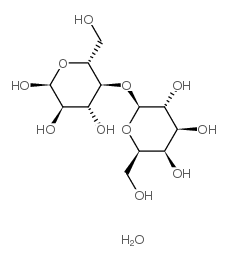 |
D-(+)-Lactose Monohydrate
CAS:64044-51-5 |
|
 |
D-(+)-Trehalose dihydrate
CAS:6138-23-4 |
|
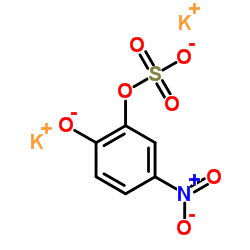 |
Dipotassium 5-nitro-2-oxidophenyl sulfate
CAS:14528-64-4 |