| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
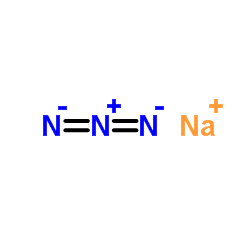 |
Sodium azide
CAS:26628-22-8 |
|
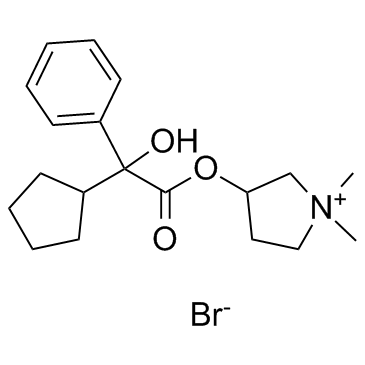 |
Glycopyrrolate
CAS:596-51-0 |
|
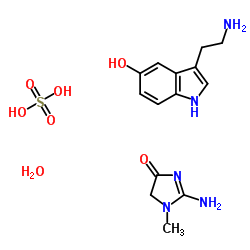 |
SEROTONIN CREATININE SULFATE MONOHYDRATE
CAS:61-47-2 |
|
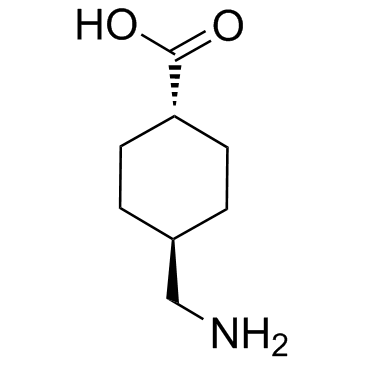 |
Tranexamic acid
CAS:1197-18-8 |
|
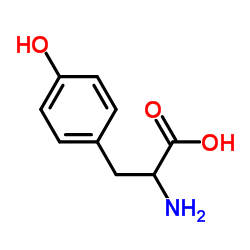 |
DL-Tyrosine
CAS:556-03-6 |
|
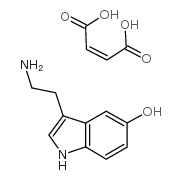 |
Serotonin hydrogen maleate
CAS:18525-25-2 |