| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
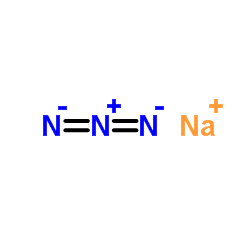 |
Sodium azide
CAS:26628-22-8 |
|
 |
Dimethyl sulfoxide
CAS:67-68-5 |
|
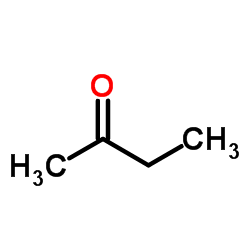 |
2-Butanone
CAS:78-93-3 |
|
 |
L-Glutamine
CAS:56-85-9 |
|
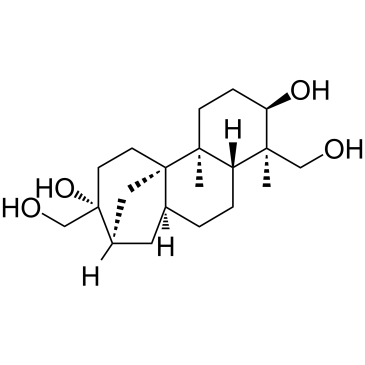 |
(+)-Aphidicolin
CAS:38966-21-1 |
|
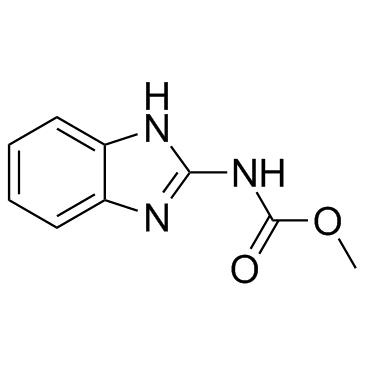 |
Carbendazim
CAS:10605-21-7 |
|
 |
4',6-Diamidino-2-phenylindole dihydrochloride
CAS:28718-90-3 |
|
 |
8-Octanoyloxypyrene-1,3,6-trisulfonic acid trisodium salt
CAS:115787-84-3 |