| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Hydrochloric acid
CAS:7647-01-0 |
|
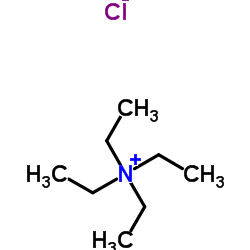 |
Tetraethylammonium chloride
CAS:56-34-8 |
|
 |
dichloroethane
CAS:107-06-2 |
|
 |
Cupric chloride
CAS:7447-39-4 |
|
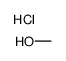 |
HYDROGEN CHLORIDE ~1.25 M IN METHANOL, 250 ML
CAS:132228-87-6 |
|
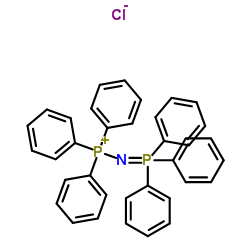 |
Bis(triphenylphosphine)iminium chloride
CAS:21050-13-5 |