| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Hydrochloric acid
CAS:7647-01-0 |
|
 |
HYDROFLUORIC ACID
CAS:7664-39-3 |
|
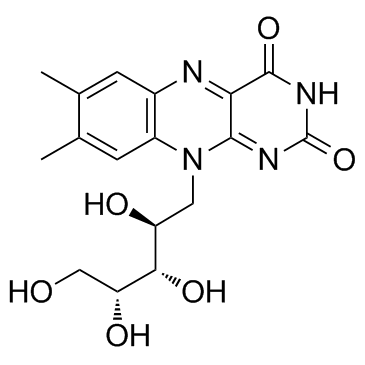 |
Riboflavine
CAS:83-88-5 |
|
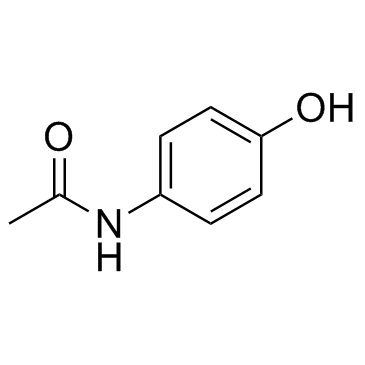 |
4-Acetamidophenol
CAS:103-90-2 |
|
 |
Ibuprofen
CAS:15687-27-1 |
|
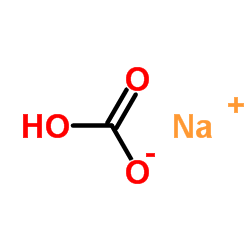 |
SodiuM bicarbonate
CAS:144-55-8 |
|
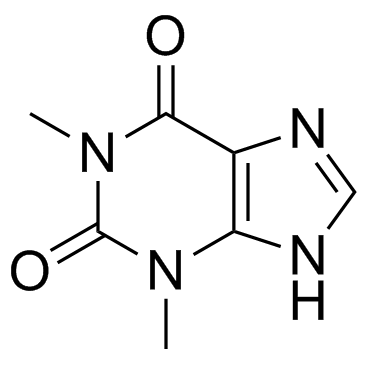 |
Theophylline
CAS:58-55-9 |
|
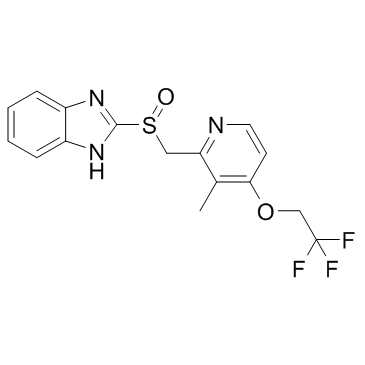 |
Lansoprazole
CAS:103577-45-3 |
|
 |
Griseofulvin
CAS:126-07-8 |
|
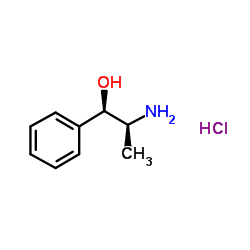 |
(1S,2R)-(+)-Norephedrine
CAS:37577-28-9 |