| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
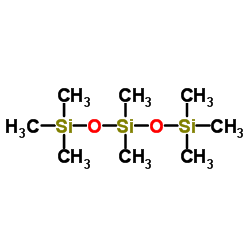 |
Octamethyltrisiloxane
CAS:107-51-7 |
|
 |
sodium chloride
CAS:7647-14-5 |
|
 |
Ethanol
CAS:64-17-5 |
|
 |
Hexamethyldisiloxane
CAS:107-46-0 |
|
 |
Acetone
CAS:67-64-1 |
|
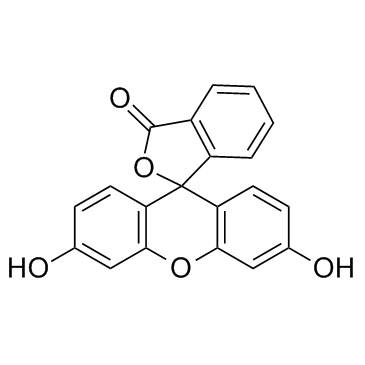 |
Fluorescein
CAS:2321-07-5 |
|
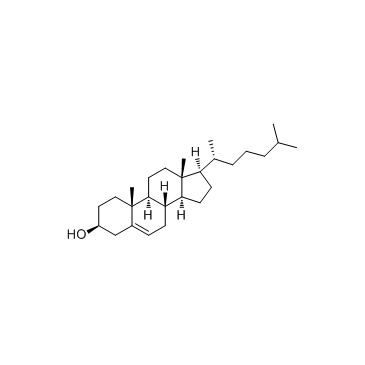 |
cholesterol
CAS:57-88-5 |
|
 |
SODIUM CHLORIDE-35 CL
CAS:20510-55-8 |
|
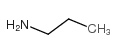 |
Propylamine
CAS:107-10-8 |
|
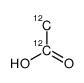 |
acetic acid
CAS:1173022-32-6 |