| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Chloroform
CAS:67-66-3 |
|
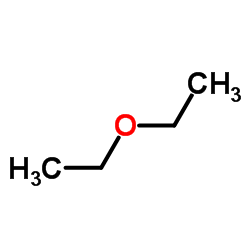 |
Diethyl ether
CAS:60-29-7 |
|
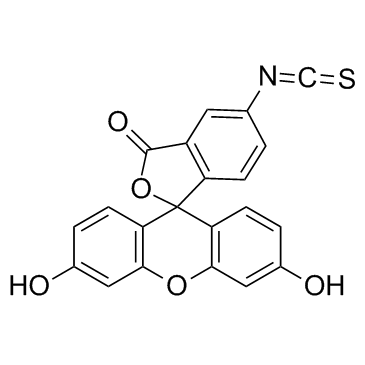 |
Fluorescein isothiocyanate
CAS:3326-32-7 |
|
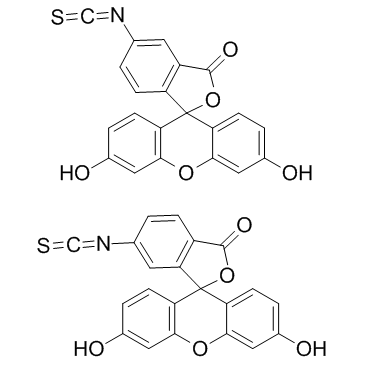 |
fluorescein 5-isothiocyanate
CAS:27072-45-3 |
|
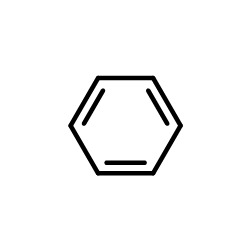 |
benzene
CAS:71-43-2 |
|
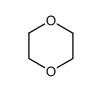 |
1,4-Dioxane
CAS:123-91-1 |
|
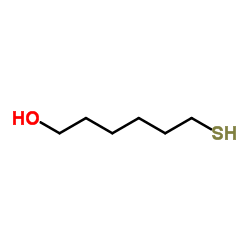 |
6-Mercapto-1-hexanol
CAS:1633-78-9 |
|
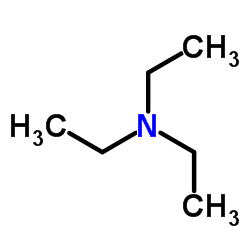 |
Triethylamine
CAS:121-44-8 |
|
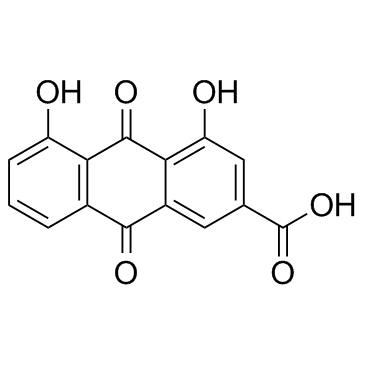 |
Rhein
CAS:478-43-3 |