| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Chloroform
CAS:67-66-3 |
|
 |
Methanol
CAS:67-56-1 |
|
 |
Dichloromethane
CAS:75-09-2 |
|
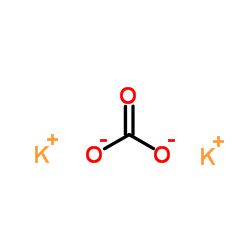 |
Potassium carbonate
CAS:584-08-7 |
|
 |
Ethanoic anhydride
CAS:108-24-7 |
|
 |
ethyl acetate
CAS:141-78-6 |
|
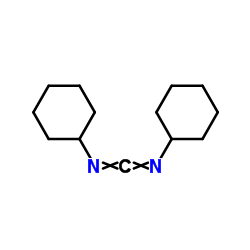 |
Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide
CAS:538-75-0 |
|
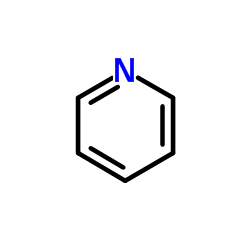 |
Pyridine
CAS:110-86-1 |
|
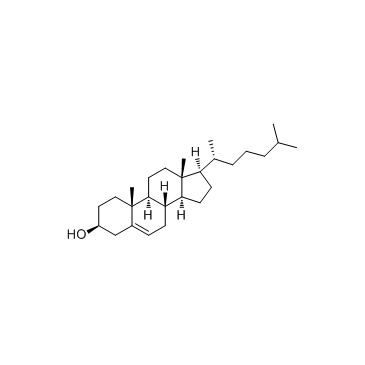 |
cholesterol
CAS:57-88-5 |
|
 |
Dihydrocholesterol
CAS:80-97-7 |