| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
1-(3-Dimethylaminopropyl)-3-ethylcarbodiimide hydrochloride
CAS:25952-53-8 |
|
 |
sodium chloride
CAS:7647-14-5 |
|
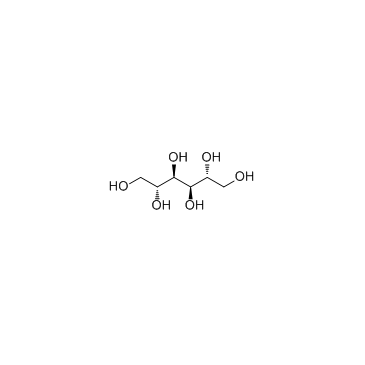 |
D-Mannitol
CAS:69-65-8 |
|
 |
dichloroethane
CAS:107-06-2 |
|
 |
Forskolin
CAS:66575-29-9 |
|
 |
Calcium chloride
CAS:10043-52-4 |
|
 |
SODIUM CHLORIDE-35 CL
CAS:20510-55-8 |
|
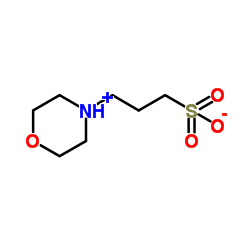 |
MOPS
CAS:1132-61-2 |
|
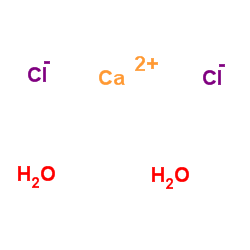 |
calcium chloride dihydrate
CAS:10035-04-8 |
|
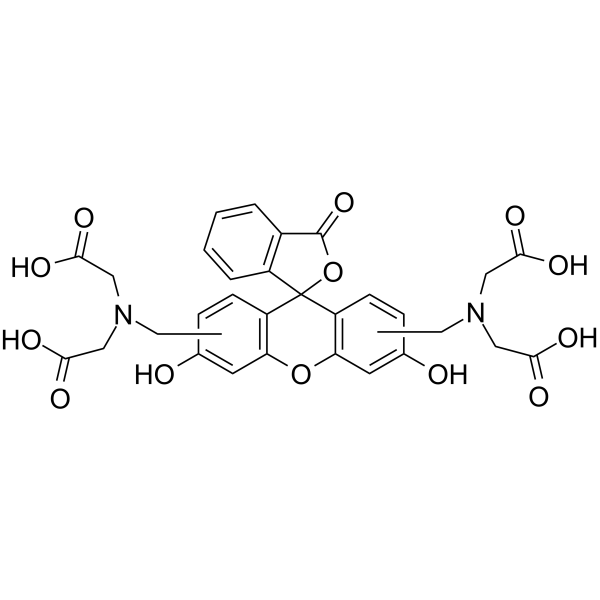 |
Calcein (mixture of isomers)
CAS:154071-48-4 |