| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
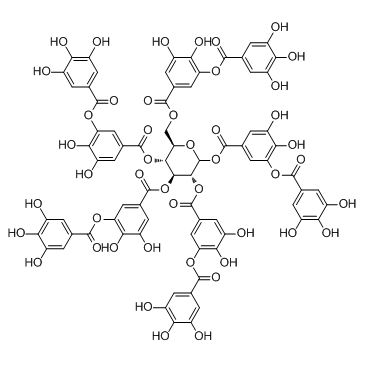 |
Tannic acid
CAS:1401-55-4 |
|
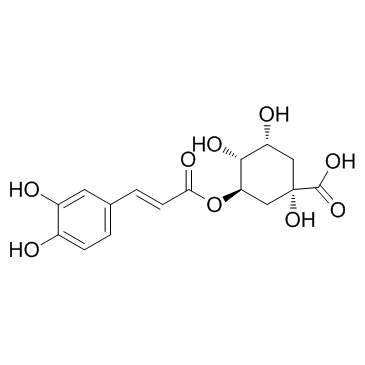 |
Chlorogenic acid
CAS:327-97-9 |
|
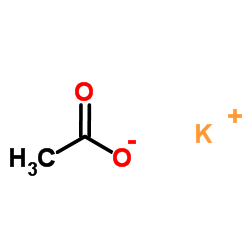 |
Potassium acetate
CAS:127-08-2 |
|
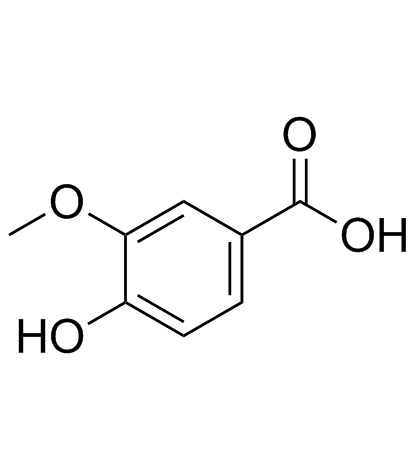 |
Vanillic acid
CAS:121-34-6 |
|
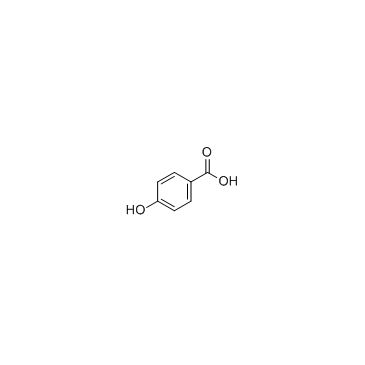 |
4-Hydroxybenzoic acid
CAS:99-96-7 |
|
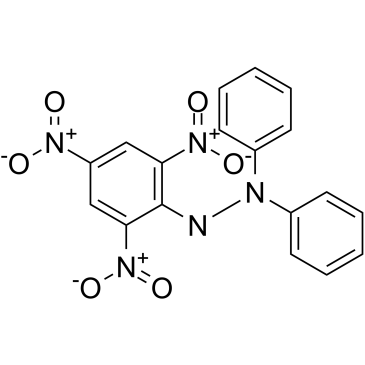 |
DPPH
CAS:1898-66-4 |
|
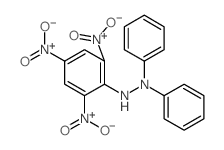 |
1,1-DIPHENYL-2-PICRYLHYDRAZINE
CAS:1707-75-1 |
|
 |
trans-4-Hydroxycinnamic acid
CAS:501-98-4 |
|
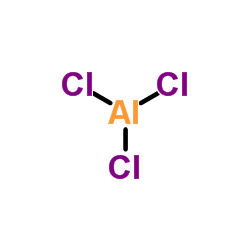 |
Aluminium chloride
CAS:7446-70-0 |
|
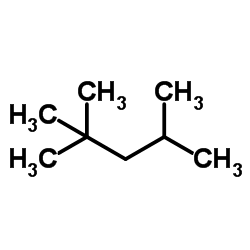 |
2,2,4-Trimethylpentane
CAS:540-84-1 |