2,2,4-Trimethylpentane
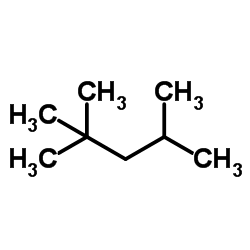
2,2,4-Trimethylpentane structure
|
Common Name | 2,2,4-Trimethylpentane | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 540-84-1 | Molecular Weight | 114.229 | |
| Density | 0.7±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 98.8±7.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C8H18 | Melting Point | -107 °C | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | -7.8±0.0 °C | |
| Symbol |




GHS02, GHS07, GHS08, GHS09 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
| Name | isooctane |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Density | 0.7±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 98.8±7.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | -107 °C |
| Molecular Formula | C8H18 |
| Molecular Weight | 114.229 |
| Flash Point | -7.8±0.0 °C |
| Exact Mass | 114.140854 |
| LogP | 4.46 |
| Vapour density | 3.9 (vs air) |
| Vapour Pressure | 45.2±0.1 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.400 |
| InChIKey | NHTMVDHEPJAVLT-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | CC(C)CC(C)(C)C |
| Stability | Stable. Highly flammable. Incompatible with oxidizing agents, reducing agents. |
| Water Solubility | INSOLUBLE |
| Freezing Point | -107.52℃ |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
MUTATION DATA
|
| Symbol |




GHS02, GHS07, GHS08, GHS09 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Danger |
| Hazard Statements | H225-H304-H315-H336-H410 |
| Precautionary Statements | P210-P261-P273-P301 + P310-P331-P501 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Faceshields;full-face respirator (US);Gloves;multi-purpose combination respirator cartridge (US);type ABEK (EN14387) respirator filter |
| Hazard Codes | F:Flammable;Xn:Harmful;N:Dangerousfortheenvironment; |
| Risk Phrases | R11;R38;R50/53;R65;R67 |
| Safety Phrases | S9-S16-S29-S33-S60-S61-S62 |
| RIDADR | UN 1262 3/PG 2 |
| WGK Germany | 1 |
| RTECS | SA3320000 |
| Packaging Group | II |
| Hazard Class | 3 |
| Precursor 10 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 10 | |
|
Serum PCB levels in a representative sample of the Spanish adult population: the BIOAMBIENT.ES project.
Sci. Total Environ. 493 , 834-44, (2014) This manuscript presents the levels of six indicator polychlorinated biphenyl (PCB) congeners (IUPAC nos. 28, 52, 101, 138, 153 and 180) in the serum of 1880 individuals from a representative sample o... |
|
|
Polypropylene membrane coated with carbon nanotubes functionalized with chitosan: Application in the microextraction of polychlorinated biphenyls and polybrominated diphenyl ethers from environmental water samples.
J. Chromatogr. A. 1408 , 56-62, (2015) Acid oxidized multi-walled carbon nanotubes (CNTs) functionalized with chitosan were coated on polypropylene membrane and used as sorbent to extract trace polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) and polybrom... |
|
|
Optimization of supercritical fluid consecutive extractions of fatty acids and polyphenols from Vitis vinifera grape wastes.
J. Food Sci. 80(1) , E101-7, (2015) In this study, supercritical fluid extraction has been successfully applied to a sequential fractionation of fatty acids and polyphenols from wine wastes (2 different vitis vinifera grapes). To this a... |
| 2,4,4-Trimethylpentane |
| EINECS 208-759-1 |
| Isobutyltrimethylmethane |
| Pentane, 2,2,4-trimethyl- |
| trimethyl isobutyl methane |
| iso-octane |
| Isooctane |
| MFCD00008943 |
| ASTM D-471 fuel A |
| Pentane,2,2,4-trimethyl |
| 2,2,4-TRIMETHYL-[1,4,2]OXAZASILINANE |
| 2, 2, 4-Trimethylpentane |
| 2,2,4-Trimethylpentane |
| 2,2,4-trimethyl-pentane |
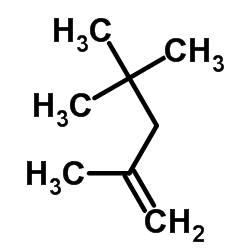 CAS#:107-39-1
CAS#:107-39-1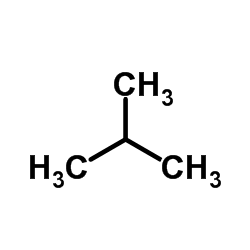 CAS#:75-28-5
CAS#:75-28-5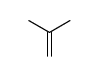 CAS#:115-11-7
CAS#:115-11-7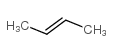 CAS#:107-01-7
CAS#:107-01-7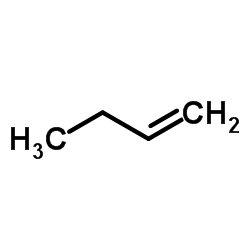 CAS#:106-98-9
CAS#:106-98-9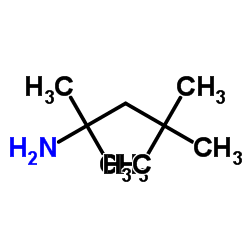 CAS#:107-45-9
CAS#:107-45-9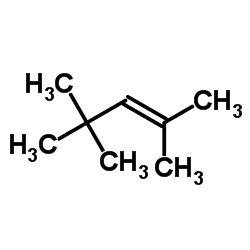 CAS#:107-40-4
CAS#:107-40-4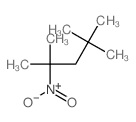 CAS#:5342-78-9
CAS#:5342-78-9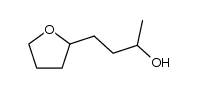 CAS#:3208-43-3
CAS#:3208-43-3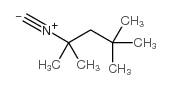 CAS#:14542-93-9
CAS#:14542-93-9 CAS#:95-93-2
CAS#:95-93-2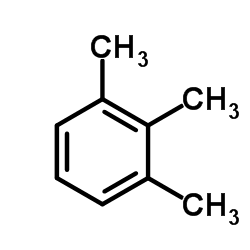 CAS#:526-73-8
CAS#:526-73-8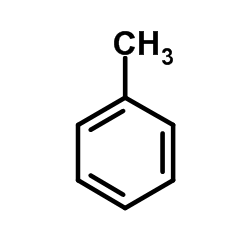 CAS#:108-88-3
CAS#:108-88-3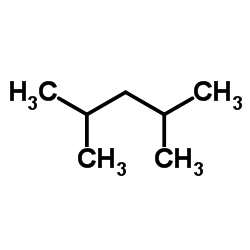 CAS#:108-08-7
CAS#:108-08-7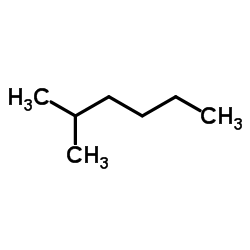 CAS#:591-76-4
CAS#:591-76-4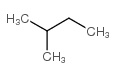 CAS#:78-78-4
CAS#:78-78-4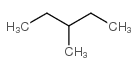 CAS#:96-14-0
CAS#:96-14-0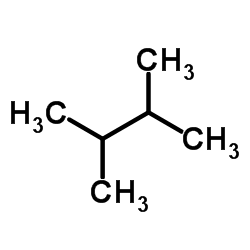 CAS#:79-29-8
CAS#:79-29-8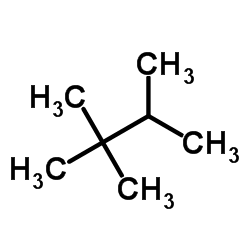 CAS#:464-06-2
CAS#:464-06-2