| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Formic Acid
CAS:64-18-6 |
|
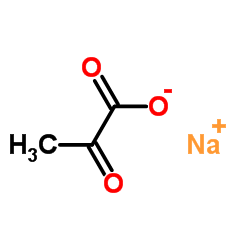 |
Sodium 2-oxopropanoate
CAS:113-24-6 |
|
 |
Methanol
CAS:67-56-1 |
|
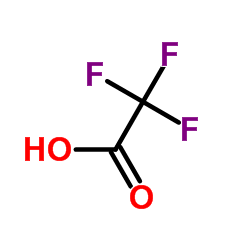 |
trifluoroacetic acid
CAS:76-05-1 |
|
 |
Dimethyl sulfoxide
CAS:67-68-5 |
|
 |
L-Glutamine
CAS:56-85-9 |
|
 |
D-(+)-Glucose
CAS:50-99-7 |
|
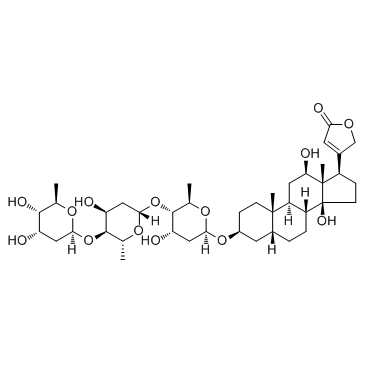 |
digoxin
CAS:20830-75-5 |
|
 |
HEPES
CAS:7365-45-9 |
|
 |
Digitoxin
CAS:71-63-6 |