| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Formic Acid
CAS:64-18-6 |
|
 |
Acetone
CAS:67-64-1 |
|
 |
Chloroform
CAS:67-66-3 |
|
 |
Acetonitrile
CAS:75-05-8 |
|
 |
Methanol
CAS:67-56-1 |
|
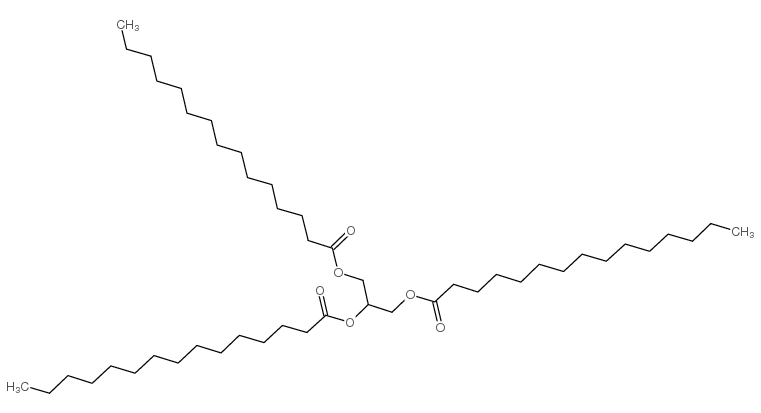 |
Tripentadecanoin
CAS:7370-46-9 |
|
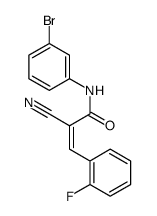 |
Lithium formate hydrate
CAS:6108-23-2 |