| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Formic Acid
CAS:64-18-6 |
|
 |
Chloroform
CAS:67-66-3 |
|
 |
sodium chloride
CAS:7647-14-5 |
|
 |
Acetonitrile
CAS:75-05-8 |
|
 |
sodium dodecyl sulfate
CAS:151-21-3 |
|
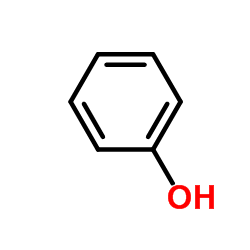 |
Phenol
CAS:108-95-2 |
|
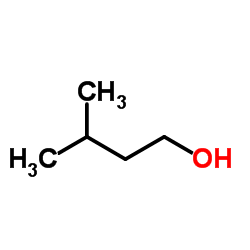 |
3-Methyl-1-butanol
CAS:123-51-3 |
|
 |
SODIUM CHLORIDE-35 CL
CAS:20510-55-8 |
|
 |
Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid
CAS:60-00-4 |
|
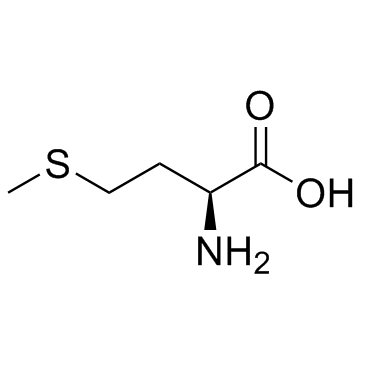 |
L-Methionine
CAS:63-68-3 |