| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
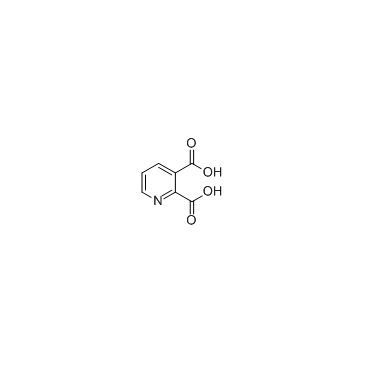 |
Quinolinic acid
CAS:89-00-9 |
|
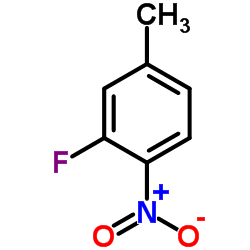 |
3-Fluoro-4-nitrotoluene
CAS:446-34-4 |
|
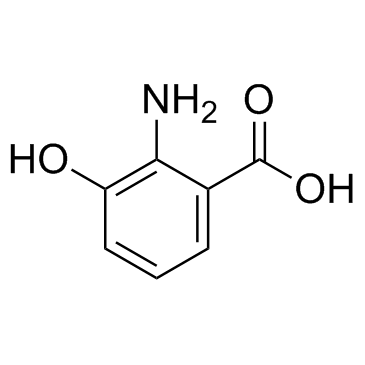 |
3-Hydroxyanthranilic acid
CAS:548-93-6 |