| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
sodiumborohydride
CAS:16940-66-2 |
|
 |
Formic Acid
CAS:64-18-6 |
|
 |
Hydrochloric acid
CAS:7647-01-0 |
|
 |
Sodium hydroxide
CAS:1310-73-2 |
|
 |
Acetonitrile
CAS:75-05-8 |
|
 |
Methanol
CAS:67-56-1 |
|
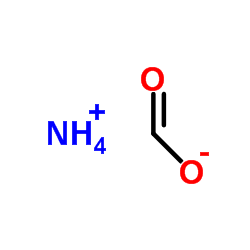 |
Formic acid ammonium salt
CAS:540-69-2 |
|
 |
Selenium
CAS:7782-49-2 |
|
 |
3-Ethyl-2,4-pentanedione
CAS:1540-34-7 |
|
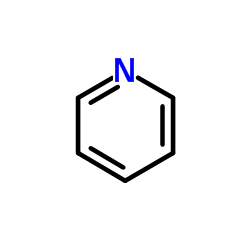 |
Pyridine
CAS:110-86-1 |