| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
sodiumborohydride
CAS:16940-66-2 |
|
 |
4-Propylphenol
CAS:645-56-7 |
|
 |
Formic Acid
CAS:64-18-6 |
|
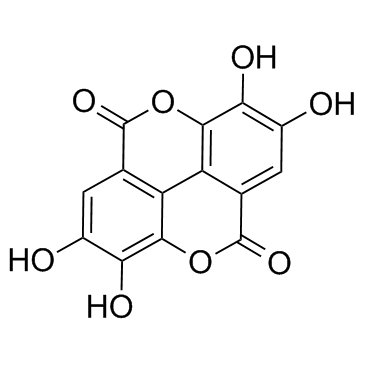 |
Ellagic acid
CAS:476-66-4 |
|
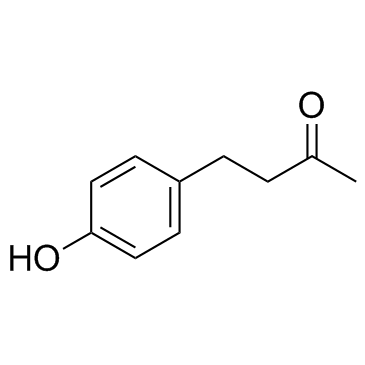 |
4-(4-Hydroxyphenyl)-2-butanone
CAS:5471-51-2 |
|
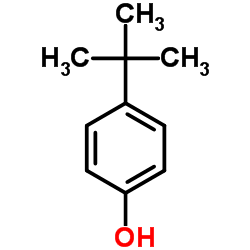 |
4-tert-Butylphenol
CAS:98-54-4 |
|
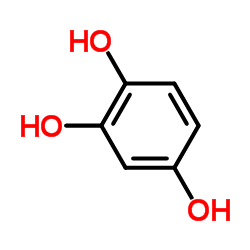 |
1,2,4-Trihydroxybenzene
CAS:533-73-3 |