| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Naringin
CAS:10236-47-2 |
|
 |
potassium chloride
CAS:7447-40-7 |
|
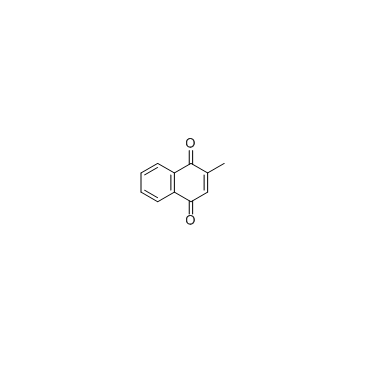 |
Menadione
CAS:58-27-5 |
|
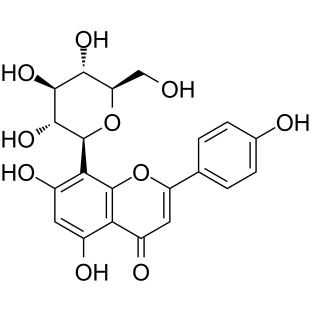 |
vitexin
CAS:3681-93-4 |
|
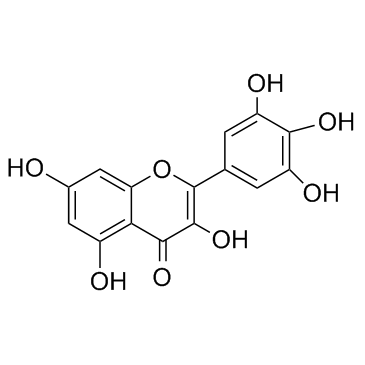 |
Myricetin
CAS:529-44-2 |
|
 |
Genistein
CAS:446-72-0 |
|
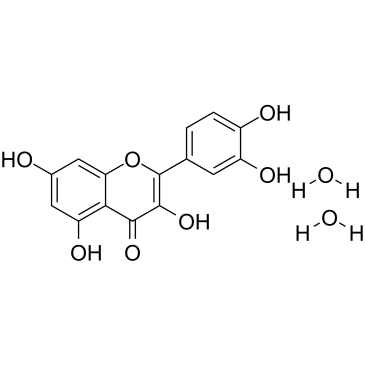 |
Quercetin dihydrate
CAS:6151-25-3 |
|
 |
(±)-Naringenin
CAS:67604-48-2 |
|
 |
Hesperidin
CAS:520-26-3 |
|
 |
Daidzein
CAS:486-66-8 |