| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
sodium carbonate
CAS:497-19-8 |
|
 |
Hydrochloric acid
CAS:7647-01-0 |
|
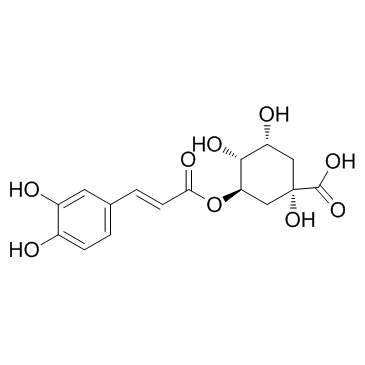 |
Chlorogenic acid
CAS:327-97-9 |
|
 |
Methanol
CAS:67-56-1 |
|
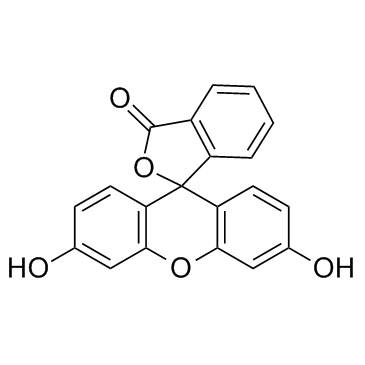 |
Fluorescein
CAS:2321-07-5 |
|
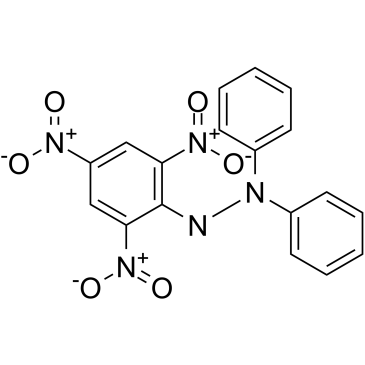 |
DPPH
CAS:1898-66-4 |
|
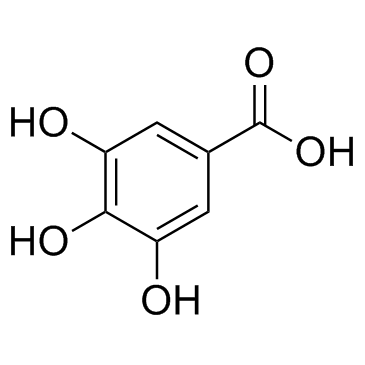 |
Gallic acid
CAS:149-91-7 |
|
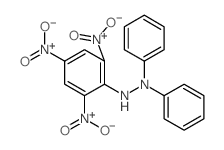 |
1,1-DIPHENYL-2-PICRYLHYDRAZINE
CAS:1707-75-1 |
|
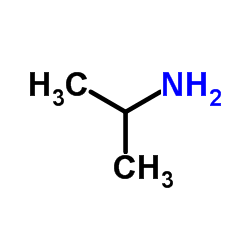 |
isopropylamine
CAS:75-31-0 |
|
 |
trans-4-Hydroxycinnamic acid
CAS:501-98-4 |