| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Sodium Fluoride
CAS:7681-49-4 |
|
 |
sodium chloride
CAS:7647-14-5 |
|
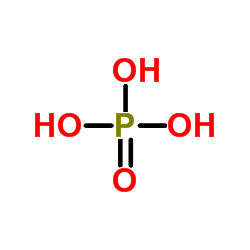 |
Phosphoric acid
CAS:7664-38-2 |
|
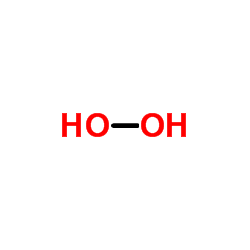 |
Hydrogen peroxide
CAS:7722-84-1 |
|
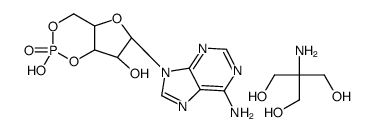 |
ADENOSINE 3':5'-CYCLIC MONOPHOSPHATE TRIS SALT
CAS:102029-77-6 |
|
 |
SODIUM CHLORIDE-35 CL
CAS:20510-55-8 |
|
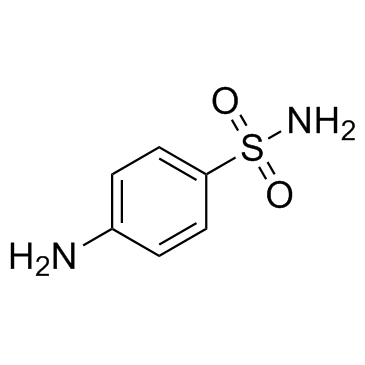 |
Sulfanilamide
CAS:63-74-1 |
|
 |
4',6-Diamidino-2-phenylindole dihydrochloride
CAS:28718-90-3 |
|
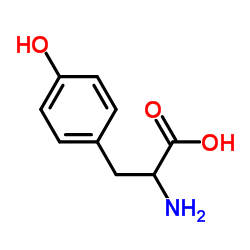 |
DL-Tyrosine
CAS:556-03-6 |
|
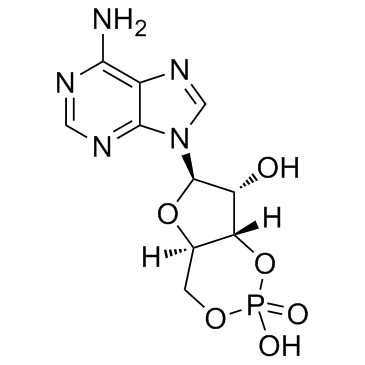 |
Adenosine cyclophosphate
CAS:60-92-4 |