| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Sodium Fluoride
CAS:7681-49-4 |
|
 |
sucrose
CAS:57-50-1 |
|
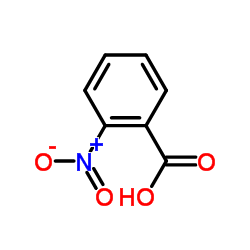 |
2-Nitrobenzoic acid
CAS:552-16-9 |
|
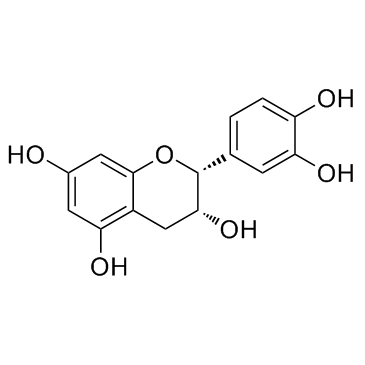 |
Epicatechin
CAS:490-46-0 |
|
 |
HEPES
CAS:7365-45-9 |
|
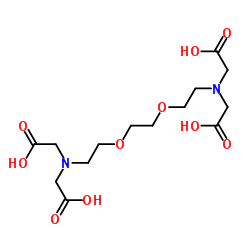 |
EGTA
CAS:67-42-5 |
|
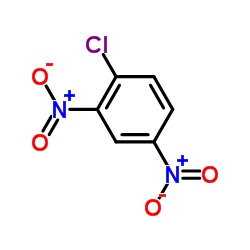 |
2,4-Dinitrochlorobenzene
CAS:97-00-7 |
|
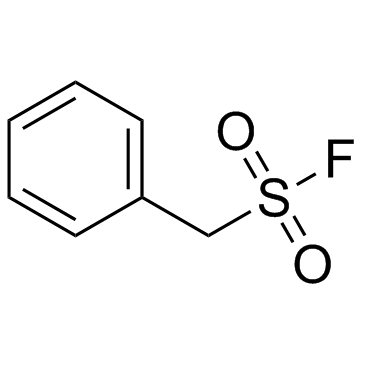 |
PMSF
CAS:329-98-6 |
|
 |
Glutathione
CAS:70-18-8 |
|
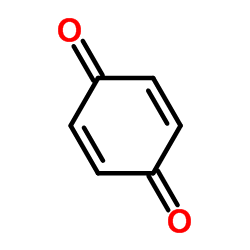 |
1,4-Benzoquinone
CAS:106-51-4 |