| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Sodium Fluoride
CAS:7681-49-4 |
|
 |
sodium chloride
CAS:7647-14-5 |
|
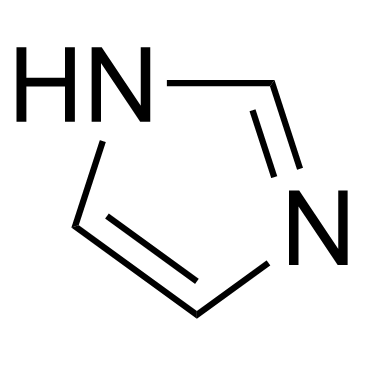 |
Imidazole
CAS:288-32-4 |
|
 |
DL-Lysine
CAS:70-54-2 |
|
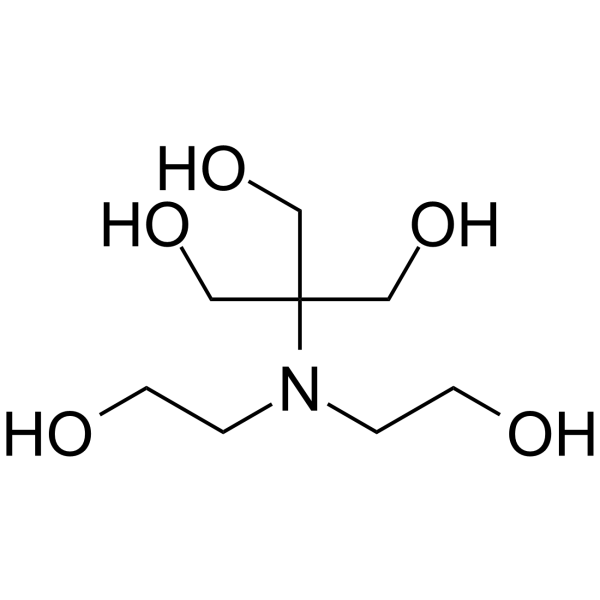 |
Bis-tris methane
CAS:6976-37-0 |
|
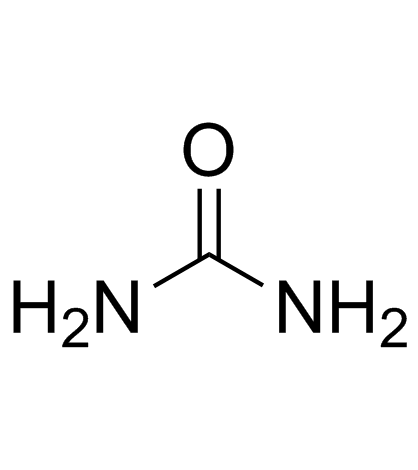 |
Urea
CAS:57-13-6 |
|
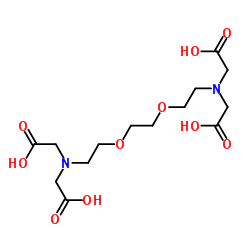 |
EGTA
CAS:67-42-5 |
|
 |
Sodium deoxycholate
CAS:302-95-4 |
|
 |
SODIUM CHLORIDE-35 CL
CAS:20510-55-8 |
|
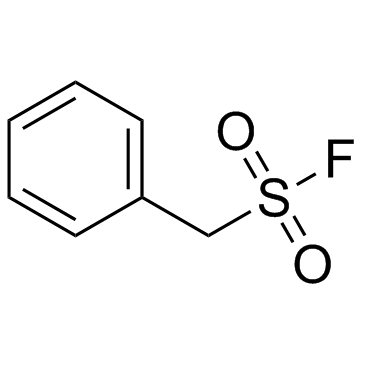 |
PMSF
CAS:329-98-6 |