| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Sulfuric acid
CAS:7664-93-9 |
|
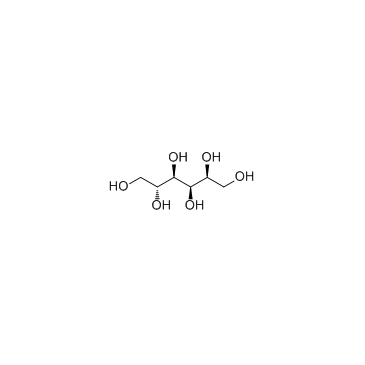 |
Sorbitol
CAS:50-70-4 |
|
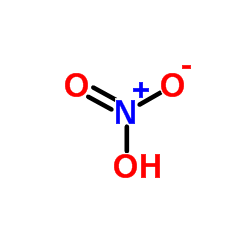 |
nitric acid
CAS:7697-37-2 |
|
 |
dichloroethane
CAS:107-06-2 |
|
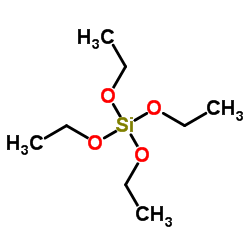 |
Tetraethyl orthosilicate
CAS:78-10-4 |
|
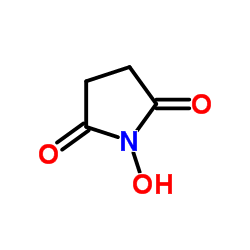 |
N-Hydroxysuccinimide
CAS:6066-82-6 |
|
 |
MES
CAS:4432-31-9 |