| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Sulfuric acid
CAS:7664-93-9 |
|
 |
Formic Acid
CAS:64-18-6 |
|
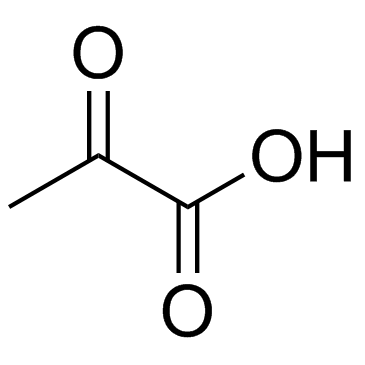 |
Pyruvic acid
CAS:127-17-3 |
|
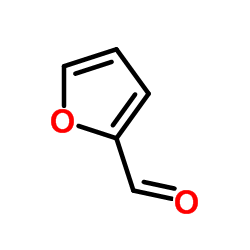 |
Furfural
CAS:98-01-1 |
|
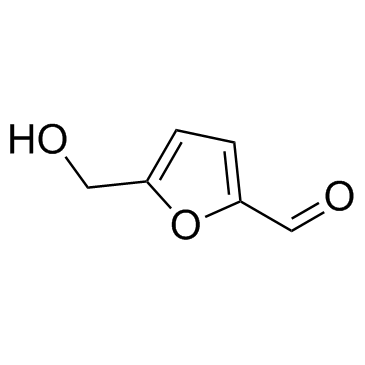 |
5-hydroxymethylfurfural
CAS:67-47-0 |