| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Sulfuric acid
CAS:7664-93-9 |
|
 |
Chloroform
CAS:67-66-3 |
|
 |
Methanol
CAS:67-56-1 |
|
 |
Formaldehyde
CAS:50-00-0 |
|
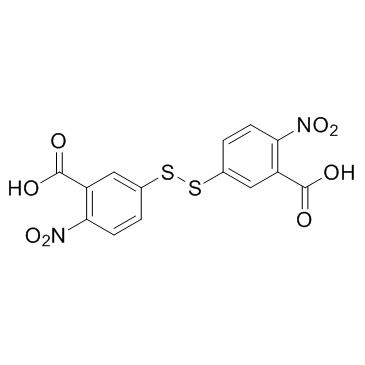 |
DTNB
CAS:69-78-3 |
|
 |
Dimethyl sulfoxide
CAS:67-68-5 |
|
 |
ethyl acetate
CAS:141-78-6 |
|
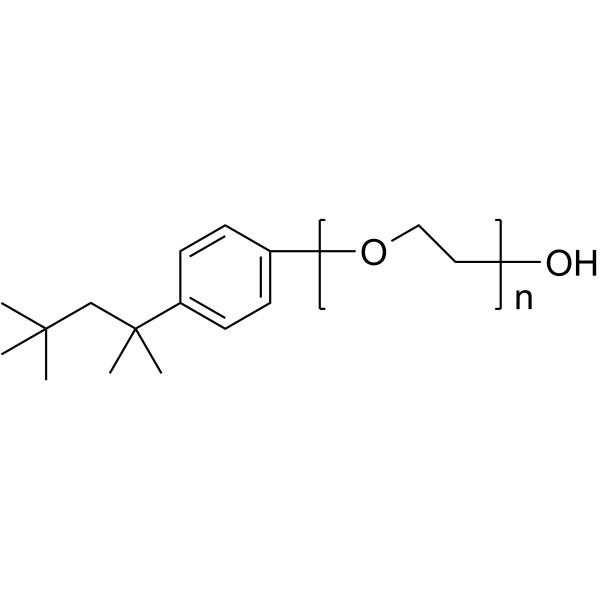 |
Triton X-100
CAS:9002-93-1 |
|
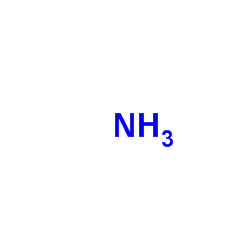 |
Ammonia
CAS:7664-41-7 |
|
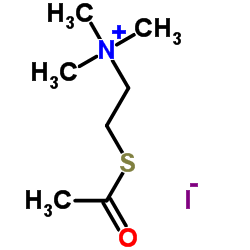 |
Acetylthiocholine Iodide
CAS:1866-15-5 |