| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Sulfuric acid
CAS:7664-93-9 |
|
 |
Ethanol
CAS:64-17-5 |
|
 |
Dichloromethane
CAS:75-09-2 |
|
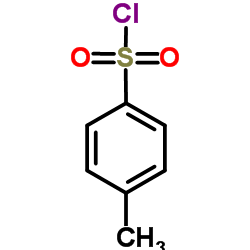 |
Tosyl chloride
CAS:98-59-9 |
|
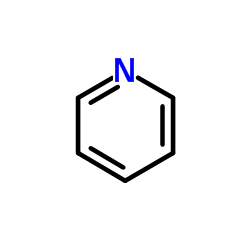 |
Pyridine
CAS:110-86-1 |
|
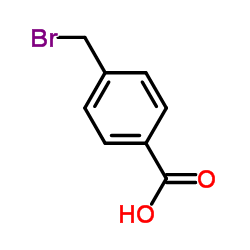 |
4-Bromomethylbenzoic acid
CAS:6232-88-8 |