| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Glycerol
CAS:56-81-5 |
|
 |
Sodium hydroxide
CAS:1310-73-2 |
|
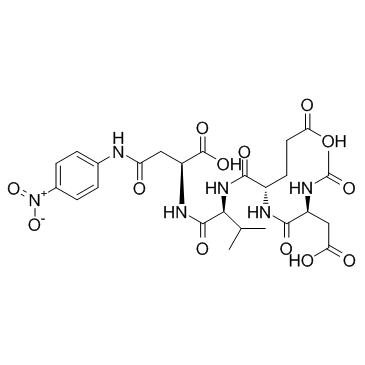 |
Ac-Asp-Glu-Val-Asp-pNA
CAS:189950-66-1 |
|
 |
Dimethyl sulfoxide
CAS:67-68-5 |
|
 |
3-Ethyl-2,4-pentanedione
CAS:1540-34-7 |
|
 |
L-Glutamine
CAS:56-85-9 |
|
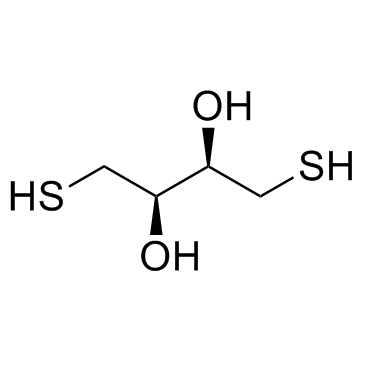 |
DL-Dithiothreitol
CAS:3483-12-3 |
|
 |
HEPES
CAS:7365-45-9 |
|
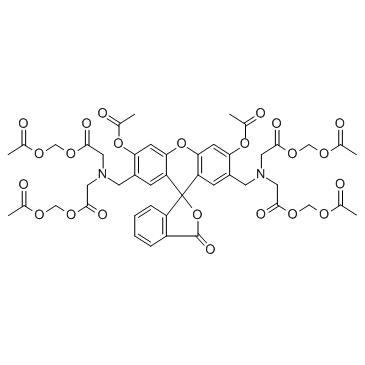 |
Calcein-AM
CAS:148504-34-1 |
|
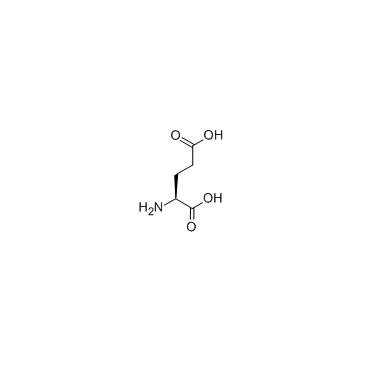 |
L-glutamic acid
CAS:56-86-0 |