| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Glycerol
CAS:56-81-5 |
|
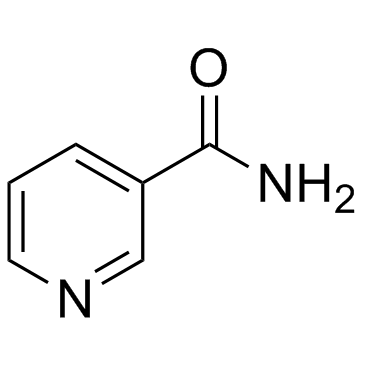 |
Nicotinamide
CAS:98-92-0 |
|
 |
sodium dodecyl sulfate
CAS:151-21-3 |
|
 |
D-(+)-Glucose
CAS:50-99-7 |
|
 |
Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid
CAS:60-00-4 |
|
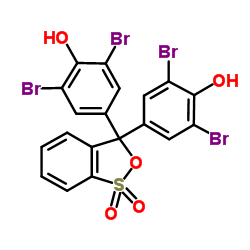 |
Bromophenol Blue
CAS:115-39-9 |
|
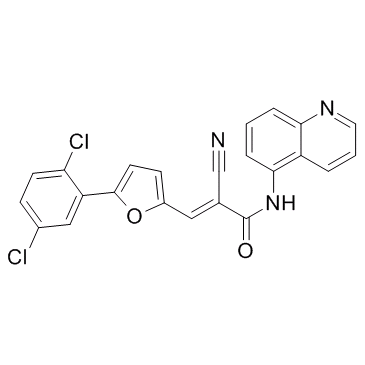 |
AGK2
CAS:304896-28-4 |