银杏酸C15:1
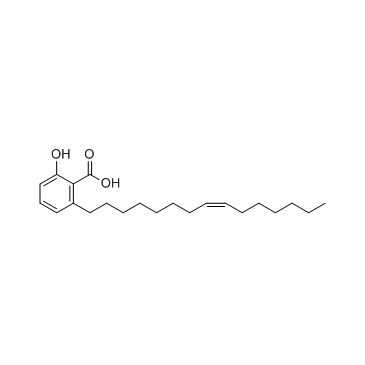
银杏酸C15:1结构式

|
常用名 | 银杏酸C15:1 | 英文名 | Ginkgolic acid C15:1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS号 | 22910-60-7 | 分子量 | 346.504 | |
| 密度 | 1.0±0.1 g/cm3 | 沸点 | 492.1±40.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| 分子式 | C22H34O3 | 熔点 | 136-137ºC | |
| MSDS | 中文版 美版 | 闪点 | 265.5±23.8 °C | |
| 符号 |

GHS07 |
信号词 | Warning |
银杏酸C15:1用途Ginkgolic Acid 是一种天然化合物,能够引起体内/体外蛋白类泛素化,但不影响体内泛素化。 |
| 中文名 | 银杏酸 C15:1 |
|---|---|
| 英文名 | 2-hydroxy-6-[(Z)-pentadec-8-enyl]benzoic acid |
| 中文别名 | 白果新酸 | 银杏酸(C15:1) | 银杏酸 | 银杏酸 | 银杏黄酮 |
| 英文别名 | 更多 |
| 描述 | Ginkgolic Acid 是一种天然化合物,能够引起体内/体外蛋白类泛素化,但不影响体内泛素化。 |
|---|---|
| 相关类别 | |
| 体外研究 | 银杏酸抑制RanGAP1-C2的体外SUMO化,IC50值为3.0μM。通过银杏酸处理,SUMO化的p53水平显着降低。重要的是,银杏酸不会影响细胞中的蛋白质泛素化。银杏酸以剂量依赖的方式抑制E1和GA-BODIPY之间的结合[1]。与阴性对照相比,银杏酸(31.2μg/ mL)抑制HIV蛋白酶活性60%,并且效果是浓度依赖性的。银杏酸处理(50和100μg/ mL)有效抑制人PBMC细胞中的HIV感染。浓度高达150μg/ mL的银杏酸不会对Jurkat细胞产生任何明显的细胞毒性[2]。 GA仅以剂量和时间依赖性方式抑制肿瘤细胞系的生长。肿瘤细胞用GA处理72小时,70.53±4.54%Hep-2和63.5±7.2%Tca8113细胞在GO/G1期延迟,凋亡百分比分别为40.4±1.58和38.4±1.7%。 GA处理的活化的胱天蛋白酶-3下调抗凋亡Bcl-2蛋白的表达并上调促凋亡Bax蛋白的表达,最终导致人PBMC细胞中肿瘤细胞中Bcl-2/Bax比率的降低。浓度高达150μg/ mL的银杏酸在Jurkat细胞中不会引起任何明显的细胞毒性[3]。 |
| 细胞实验 | 将Jurkat细胞(106细胞/ mL)在含有或不含有不同浓度银杏酸的RPMI培养基中培养48小时,以测试银杏酸的细胞毒性。使用四唑鎓化合物(MTS)和电子偶联剂(PMS)测定银杏酸的细胞毒性。 MTS被细胞化学还原成甲,其可溶于组织培养基中。甲氮的吸光度的测量可以使用96孔微孔板在492nm下进行。由于甲production的产生与活细胞的数量成比例,所产生的颜色的强度是细胞活力的良好指示。 |
| 参考文献 |
| 密度 | 1.0±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| 沸点 | 492.1±40.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| 熔点 | 136-137ºC |
| 分子式 | C22H34O3 |
| 分子量 | 346.504 |
| 闪点 | 265.5±23.8 °C |
| 精确质量 | 346.250793 |
| PSA | 57.53000 |
| LogP | 9.44 |
| 外观性状 | 白色粉末 |
| 蒸汽压 | 0.0±1.3 mmHg at 25°C |
| 折射率 | 1.527 |
| 储存条件 | 2-8 °C, 密封, 干燥, 避光 |
| 符号 |

GHS07 |
|---|---|
| 信号词 | Warning |
| 危害声明 | H315-H319-H335 |
| 警示性声明 | P261-P305 + P351 + P338 |
| 个人防护装备 | dust mask type N95 (US);Eyeshields;Gloves |
| 危害码 (欧洲) | Xi:Irritant; |
| 风险声明 (欧洲) | R36/37/38 |
| 安全声明 (欧洲) | S26 |
| 危险品运输编码 | NONH for all modes of transport |
| 银杏酸C15:1上游产品 8 | |
|---|---|
| 银杏酸C15:1下游产品 4 | |
|
Design and evaluation of anacardic acid derivatives as anticavity agents.
Eur. J. Med. Chem. 43 , 1315-20, (2008) On the basis of antibacterial anacardic acids, 6-pentadecenylsalicylic acids, isolated from the cashew apple, Anacardium occidentale L. (Anacardiaceae), a series of 6-alk(en)ylsalicylic acids were syn... |
|
|
Cytotoxicity of ginkgolic acid in HepG2 cells and primary rat hepatocytes.
Toxicol. Lett. 187(3) , 131-6, (2009) Ginkgolic acids and related alkylphenols (e.g. cardanols and cardols) have been recognized as hazardous compounds with suspected cytotoxic, allergenic, mutagenic and carcinogenic properties. To determ... |
|
|
Identification of TRIML2, a novel p53 target, that enhances p53 SUMOylation and regulates the transactivation of proapoptotic genes.
Mol. Cancer Res. 13(2) , 250-62, (2015) The tumor-suppressor protein p53, encoded by TP53, inhibits tumorigenesis by inducing cell-cycle arrest, senescence, and apoptosis. Several genetic polymorphisms exist in TP53, including a proline to ... |
| MFCD03093717 |
| 15:1 anacardic acid |
| Ginkgolic acid |
| Ginkgolic acid 15:1 |
| Romanicardic acid |
| (Z)-2-Hydroxy-6-(pentadec-8-en-1-yl)benzoic acid |
| Ginkgolic acid (15:1) |
| 2-Hydroxy-6-(pentadec-8-en-1-yl)benzoic acid |
| (Z)-6-[8-pentadecenyl]salicylic acid |
| 2-hydroxy-6-pentadec-8(Z)-enylbenzoic acid |
| 6-[(8Z)-Pentadecenyl]-salicylic acid,Ginkgolic acid I |
| Ginkgoic acid |
| 2-hydroxy-6-(8-pentadecenyl) salicylic acid |
| Anacardic acid monoene |
| 6-(8-pentadecenyl)salicylic acid |
| 2-Hydroxy-6-[(8Z)-pentadec-8-en-1-yl]benzoic acid |
| Ginkgolic acid I |
| Gingkolic Acid |
| 2-Hydroxy-6-[(8Z)-8-pentadecen-1-yl]benzoic acid |
| 6-(8Z-pentadecenyl)salicylic acid |
| Ginkgolic acid (C15:1) |
| 6-<8(Z)-pentadecenyl>salicylic acid |
| Benzoic acid, 2-hydroxy-6-(8-pentadecenyl)-, (Z)- |
| Benzoic acid, 2-hydroxy-6-[(8Z)-8-pentadecen-1-yl]- |
| Ginkgolic Acid C15:1 |
| (Z)-2-Hydroxy-6-(8-pentadecenyl)benzoic acid |

 CAS号629-30-1
CAS号629-30-1 CAS号34335-17-6
CAS号34335-17-6 CAS号81036-11-5
CAS号81036-11-5 CAS号114802-06-1
CAS号114802-06-1 CAS号1082423-86-6
CAS号1082423-86-6 CAS号81625-30-1
CAS号81625-30-1![2-[(7-溴庚基)氧基]四氢-2H-吡喃结构式](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/180/10160-25-5.png) CAS号10160-25-5
CAS号10160-25-5 CAS号71317-70-9
CAS号71317-70-9 CAS号111-71-7
CAS号111-71-7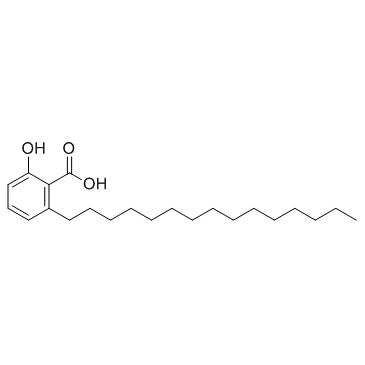 CAS号16611-84-0
CAS号16611-84-0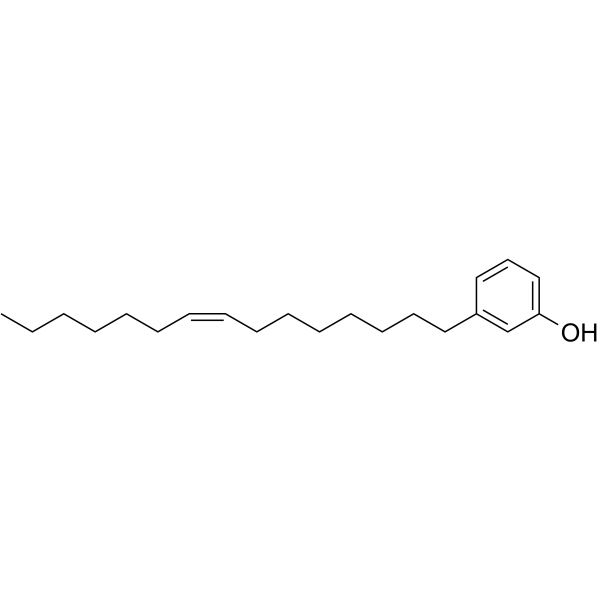 CAS号501-26-8
CAS号501-26-8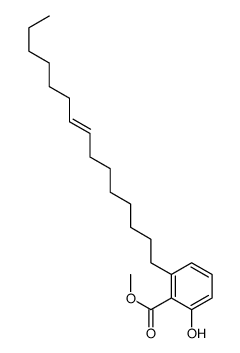 CAS号58682-65-8
CAS号58682-65-8
