Inhibition of S37 ascites cell amino acid transport systems by alpha-chloromethylketone analogs.
R H Matthews, N J Lewis, J Hes, J H Im, G Milo
文献索引:Biochim. Biophys. Acta 601(3) , 640-53, (1980)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
Alanine chloromethylketone and leucine chloromethylketone were synthesized and their effects on amino acid transport in sarcoma 37 mirone ascites tumor (S37) cells were studied. Alanine chloromethylketone preincubation weakly inhibited system A. Leucine chloromethylketone preincubation strongly inhibited both amino acid transport systems L and A. Leucine chloromethylketone was also a competitive inhibitor of leucine transport. Labeled leucine chloromethylketone was concentrated by S37 cells. Leucine chloromethylketone preincubation inhibition was concentration dependent and partial protection of transport was afforded by leucine. Steady-state retention of amino acids was decreased more than the initial velocity of transport by leucine chloromethylketone preincubation. Glutathione was also depleted. Labeled leucine chloromethylketone was incorporated in a plasma membrane protein fraction comigrating on a DEAE-cellulose column (DE52) with gamma-glutamyltranspeptidase activity. There was a modest increase in vital staining after treatment of S37 cells with leucine chloromethylketone, and glucose uptake was also inhibited. Whilst several effects occur during treatment of S37 cells with leucine chloromethylketone, it is suggested than one prominent effect is alkylation of amino acid transport system components.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
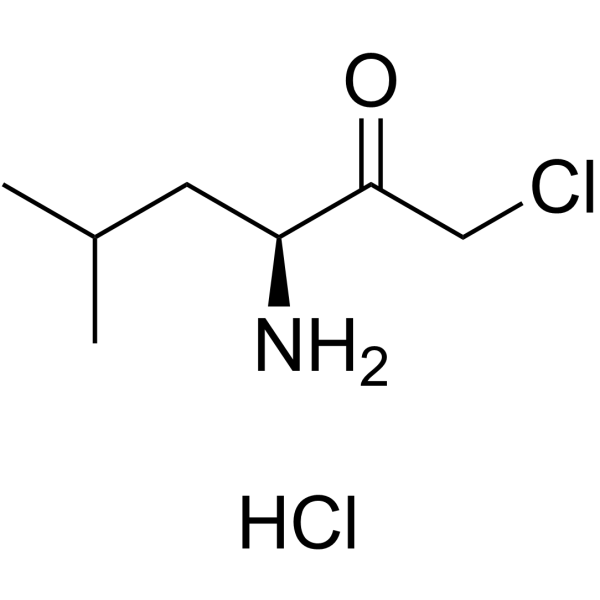 |
H-Leu-CMK.HCl
CAS:54518-92-2 |
C7H15Cl2NO |
|
Acylpeptide hydrolase: inhibitors and some active site resid...
1992-02-25 [J. Biol. Chem. 267 , 3811-3818, (1992)] |
|
Acetylleucine chloromethyl ketone, an inhibitor of acylpepti...
1999-09-16 [Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 263 , 139-142, (1999)] |
|
Chloromethyl ketones are insulin-like stimulators of lipid s...
1998-01-01 [Arch. Insect Biochem. Physiol. 39 , 9-17, (1998)] |
|
Metabolism and degradation products of recombinant human ins...
1999-03-01 [Xenobiotica 29 , 281-295, (1999)] |
|
[14C]leucine chloromethylketone interaction with sarcoma 37 ...
1982-01-01 [Cancer Lett. 16(2) , 207-18, (1982)] |