| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
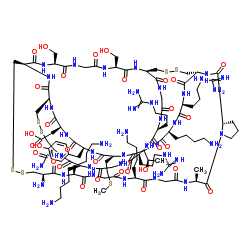 |
ω-芋螺毒素MVIIC
CAS:147794-23-8 |
|
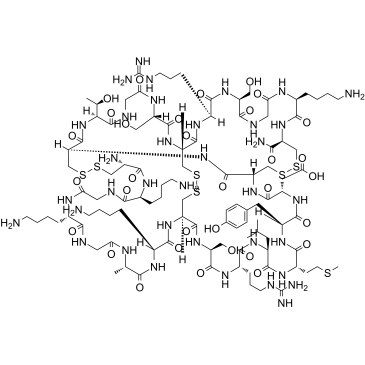 |
醋酸齐考诺肽
CAS:107452-89-1 |