Izvestiia Akademii nauk. Seriia biologicheskaia / Rossiiskaia akademiia nauk
1994-01-01
[The stacking interaction of antibiotics of the pyrimido[5,4-e]-1,2,4-triazine series with purines].
V L Antonovskiĭ
文献索引:Izv. Akad. Nauk Ser. Biol. (1) , 145-7, (1994)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
The changes in the PMR spectra of purine bases added to aqueous solutions (D2O) of antibiotics of the pyrimido[5,4-e]-1,2,4-triazine type, reumycin and xanthotricin as well as the changes in the PMR indicate formation of heteroassociates with batch structure as a result of stacking interaction. Chemotherapeutic effect of the antibiotics is explained by their intercalation into the batches of the nucleic acids bases, which violates their functioning.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
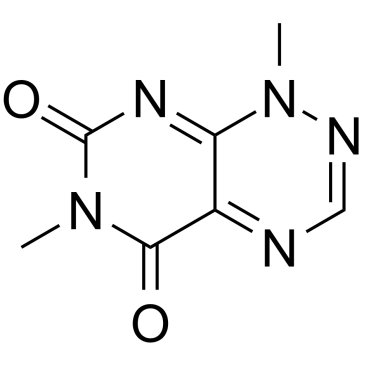 |
毒黄素
CAS:84-82-2 |
C7H7N5O2 |
相关文献:
更多...
|
Investigations into the Biosynthesis, Regulation, and Self-R...
2015-08-17 [ChemBioChem. 16 , 1782-90, (2015)] |
|
The quorum sensing-dependent gene katG of Burkholderia gluma...
2009-07-01 [J. Bacteriol. 191(13) , 4152-7, (2009)] |
|
Identification of the product of toxoflavin lyase: degradati...
2012-03-21 [J. Am. Chem. Soc. 134(11) , 5326-30, (2012)] |
|
Structural and functional analysis of phytotoxin toxoflavin-...
2011-01-01 [PLoS ONE 6(7) , e22443, (2011)] |
|
Simultaneous determination of toxic metabolites by linear co...
1991-09-01 [Analyst 116(9) , 919-22, (1991)] |