| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
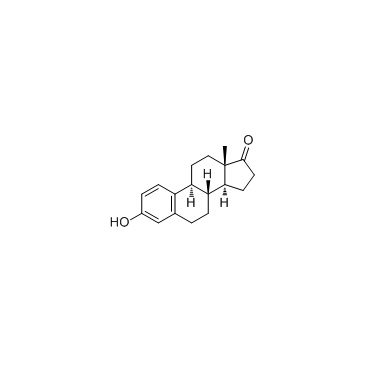 |
雌酚酮
CAS:53-16-7 |
|
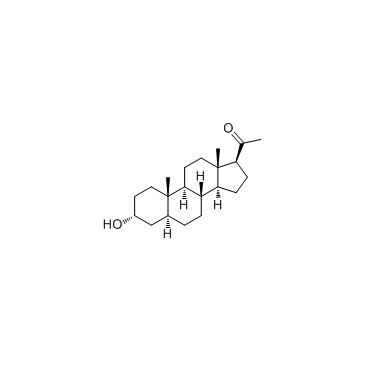 |
5alpha-孕甾-3alpha-醇-20-酮
CAS:516-54-1 |
|
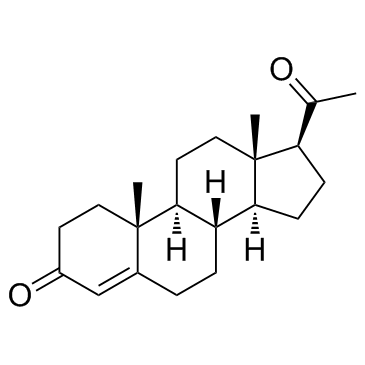 |
孕酮; 黄体素; 黄体酮
CAS:57-83-0 |
|
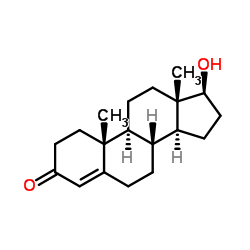 |
睾酮
CAS:58-22-0 |
|
 |
米非司酮
CAS:84371-65-3 |
|
 |
四甲基罗丹明甲酯高氯酸盐
CAS:115532-50-8 |
|
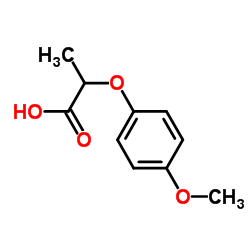 |
2-(4-甲氧基苯氧基)丙酸
CAS:13794-15-5 |
|
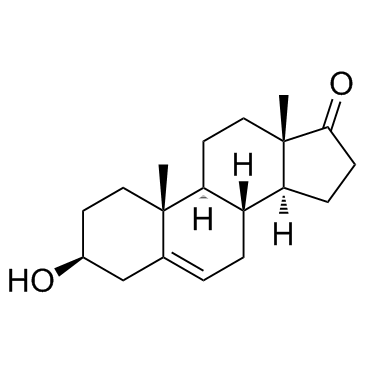 |
去氢表雄酮
CAS:53-43-0 |
|
 |
羟基氟他胺
CAS:52806-53-8 |
|
 |
5a-雄甾烷-3a,17b-二醇
CAS:1852-53-5 |