| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
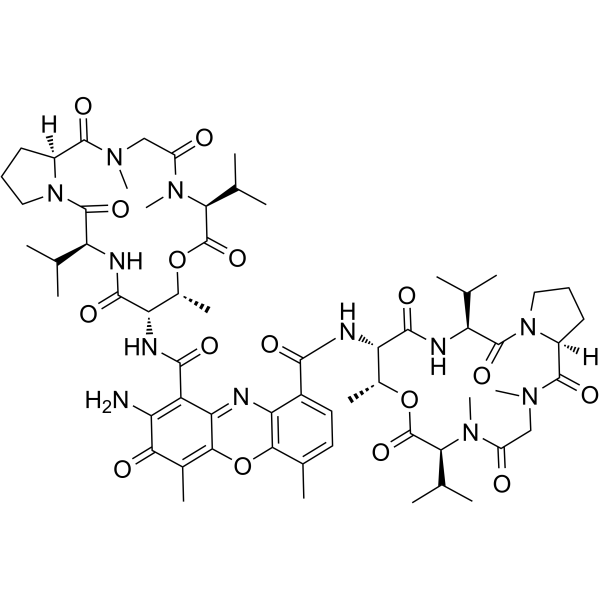 |
放线菌素D
CAS:50-76-0 |
|
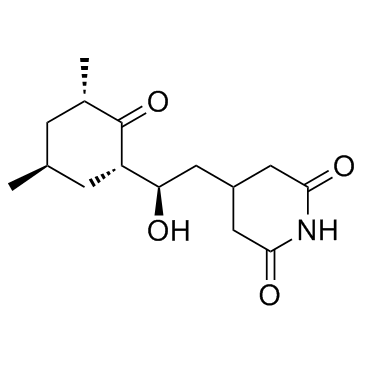 |
放线菌酮
CAS:66-81-9 |
|
 |
5-(4-氯苯基)-1-(4-甲氧基苯基)-3-(三氟甲基)-1H-吡唑
CAS:188817-13-2 |
|
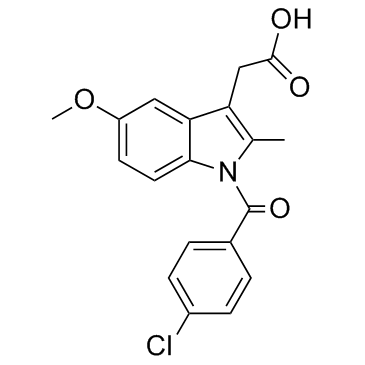 |
吲哚美辛
CAS:53-86-1 |
|
 |
塞来昔布
CAS:169590-42-5 |
|
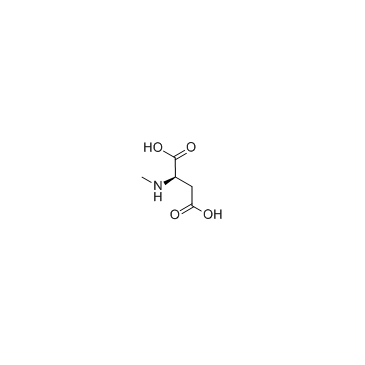 |
N-甲基-D-天冬氨酸水合物
CAS:6384-92-5 |