| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
 |
环孢霉素A
CAS:59865-13-3 |
|
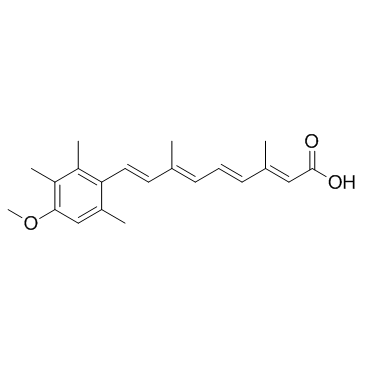 |
阿维A酸
CAS:55079-83-9 |
|
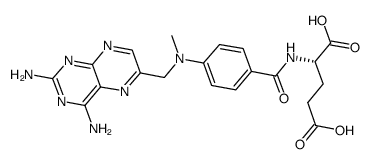 |
二水合氨甲嘌呤
CAS:133073-73-1 |
|
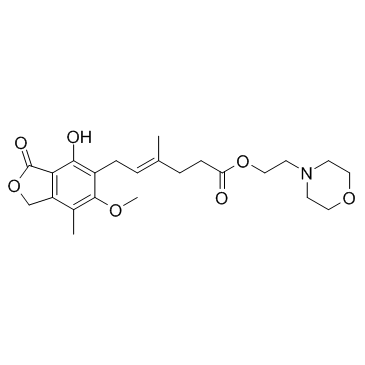 |
吗替麦考酚酯
CAS:128794-94-5 |
|
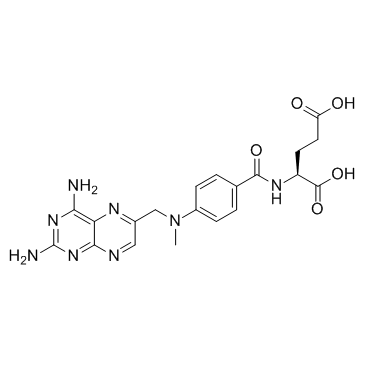 |
甲氨蝶呤
CAS:59-05-2 |
|
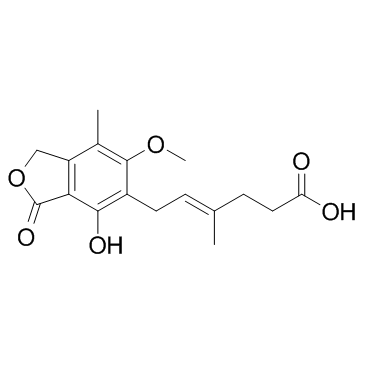 |
霉酚酸
CAS:24280-93-1 |
|
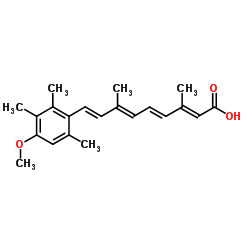 |
9-(4-甲氧基-2,3,6-三甲基苯基)-3,7-二甲基-2,4,6,8-丁烯酸
CAS:69427-46-9 |