| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
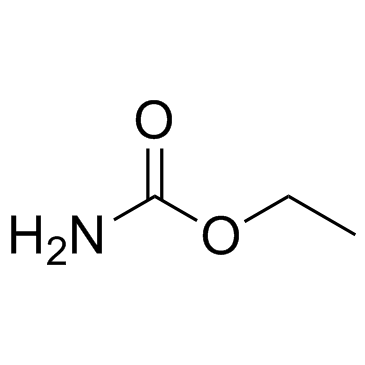 |
氨基甲酸乙酯
CAS:51-79-6 |
|
 |
蜂毒明肽
CAS:24345-16-2 |
|
 |
卡巴胆碱
CAS:51-83-2 |
|
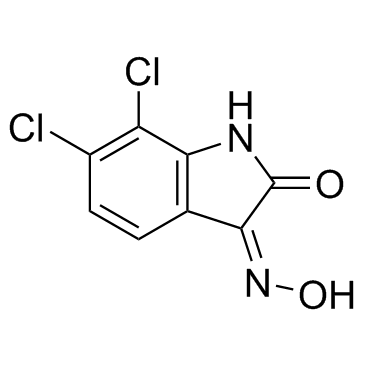 |
3-肟-6,7-二氯-1H-吲哚-2,3-二酮
CAS:18711-16-5 |