| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
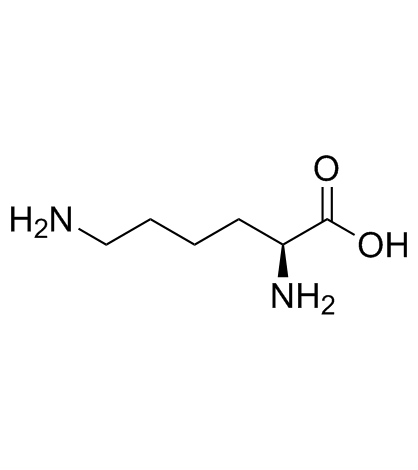 |
L-赖氨酸
CAS:56-87-1 |
|
 |
L-赖氨酸盐酸盐
CAS:657-27-2 |
|
![(R)-(-)2-(4-(4-氯苯基)-2,3,9-三甲基-6H-噻吩并[3,2-F][1,2,4]三唑并[4,3-A][1,4]二氮杂环庚烷-6-基)乙酸叔丁酯 结构式](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/075/1268524-71-5.png) |
(R)-(-)2-(4-(4-氯苯基)-2,3,9-三甲基-6H-噻吩并[3,2-F][1,2,4]三唑并[4,3-A][1,4]二氮杂环庚烷-6-基)乙酸叔丁酯
CAS:1268524-71-5 |
|
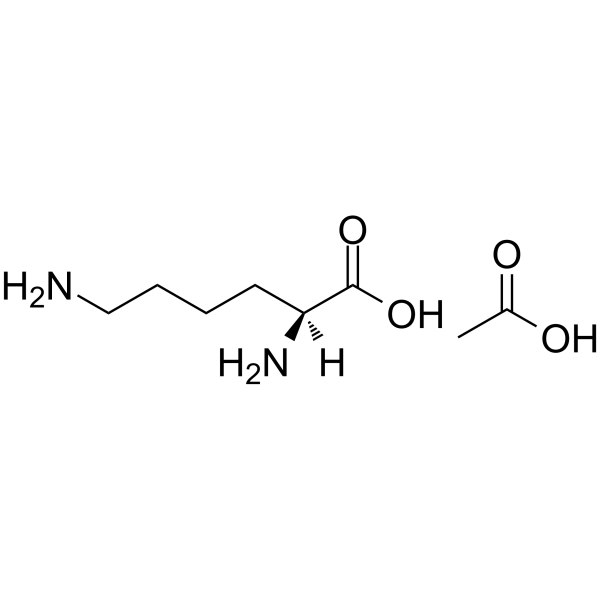 |
醋酸赖氨酸
CAS:57282-49-2 |