| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
 |
抗坏血酸
CAS:50-81-7 |
|
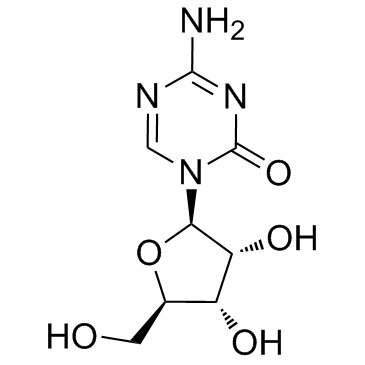 |
阿扎胞苷
CAS:320-67-2 |
|
 |
丁酸钠
CAS:156-54-7 |
|
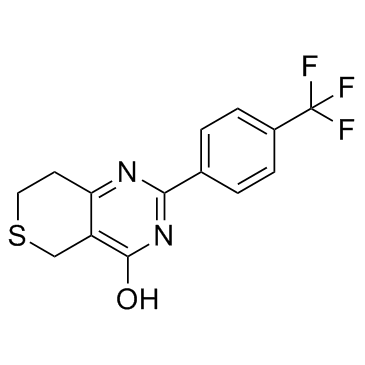 |
XAV-939
CAS:284028-89-3 |
|
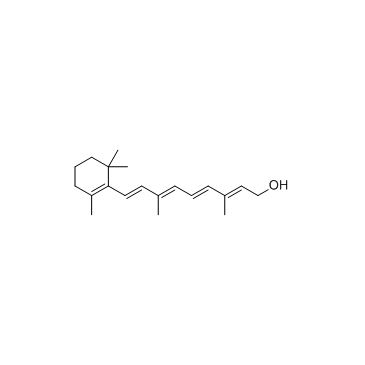 |
视黄醇
CAS:68-26-8 |
|
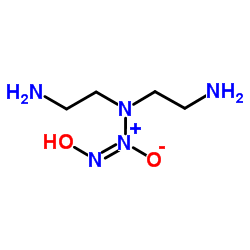 |
3,3-二(氨乙基)-1-羟基-2-羰基-1-三氮烯
CAS:146724-94-9 |