| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
 |
抗坏血酸
CAS:50-81-7 |
|
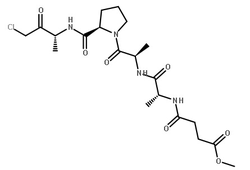 |
弹性蛋白酶,来源猪胰腺
CAS:39445-21-1 |
|
 |
胰岛素(人)
CAS:11061-68-0 |
|
 |
木瓜蛋白酶
CAS:9001-73-4 |
|
 |
弹性酶
CAS:9004-06-2 |