| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
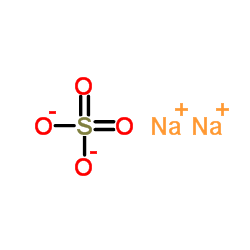 |
元明粉
CAS:7757-82-6 |
|
 |
结晶硫酸钠,十水合物
CAS:7727-73-3 |
|
 |
氯化镁
CAS:7786-30-3 |
|
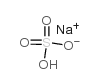 |
硫酸氢钠
CAS:7681-38-1 |
|
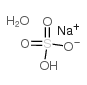 |
硫酸氢钠,一水
CAS:10034-88-5 |