| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
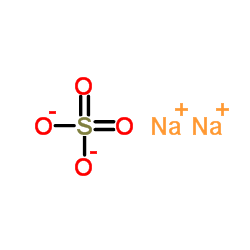 |
sodium sulfate
CAS:7757-82-6 |
|
 |
Sodium sulfate decahydrate
CAS:7727-73-3 |
|
 |
Magnesium choride
CAS:7786-30-3 |
|
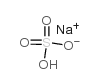 |
Sodium bisulfate
CAS:7681-38-1 |
|
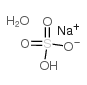 |
Sodium bisulfate monohydrate
CAS:10034-88-5 |