| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
 |
乙醇
CAS:64-17-5 |
|
 |
乙腈
CAS:75-05-8 |
|
 |
甲醇
CAS:67-56-1 |
|
 |
二氯甲烷
CAS:75-09-2 |
|
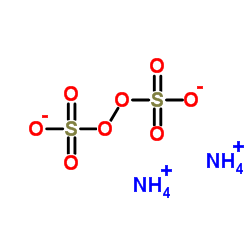 |
过硫酸铵
CAS:7727-54-0 |
|
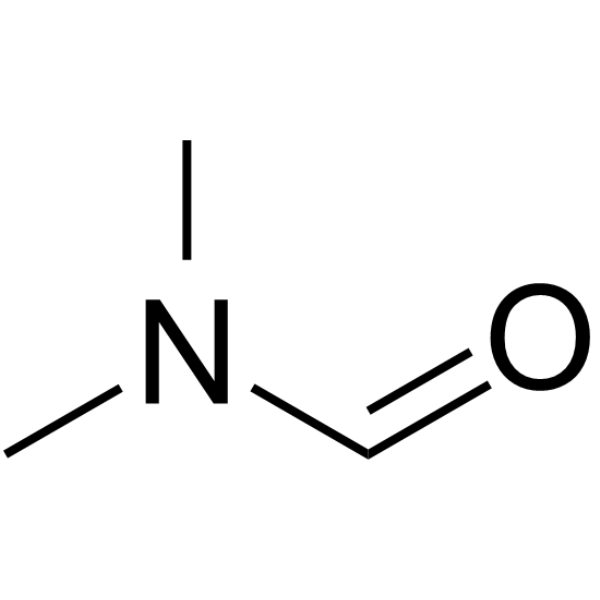 |
N,N-二甲基甲酰胺
CAS:68-12-2 |
|
 |
二甲基亚砜
CAS:67-68-5 |
|
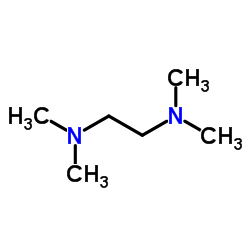 |
四甲基乙二胺(TEMED)
CAS:110-18-9 |
|
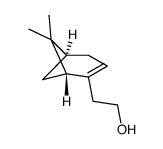 |
6,6-二甲基联环(3.1.1)庚烷-2-烯-2-乙醇
CAS:35836-73-8 |
|
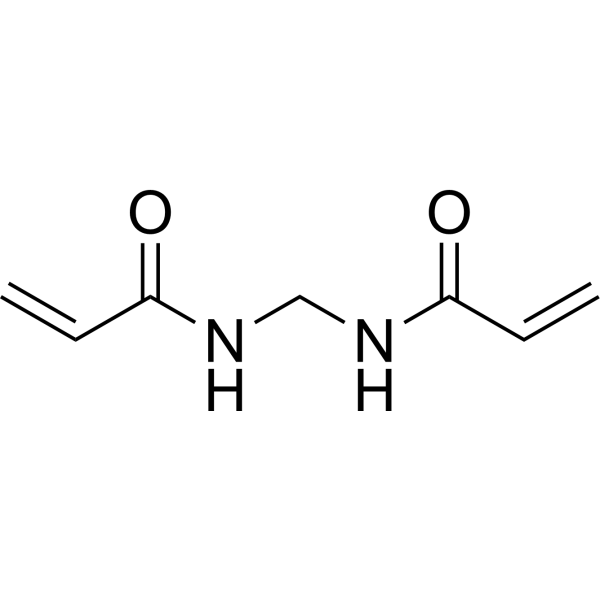 |
N,N′-亚甲基双丙烯酰胺
CAS:110-26-9 |