| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
 |
乙醇
CAS:64-17-5 |
|
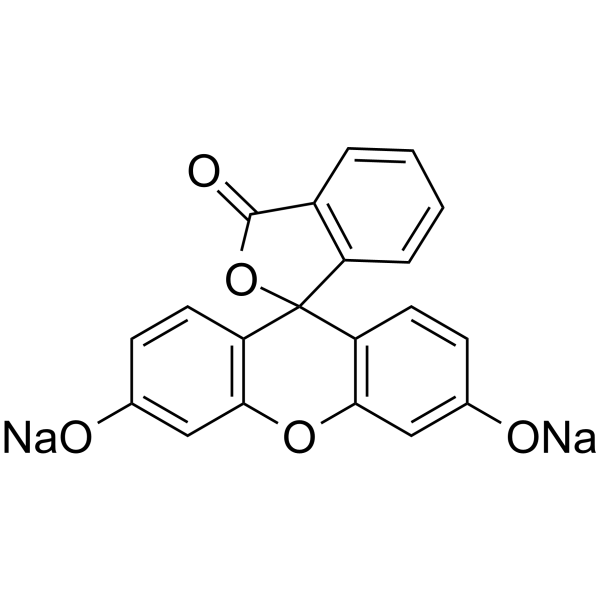 |
荧光素钠
CAS:518-47-8 |
|
 |
Nω-硝基-L-精氨酸
CAS:2149-70-4 |
|
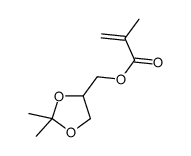 |
丙酮缩甘油异丁烯酸酯
CAS:7098-80-8 |
|
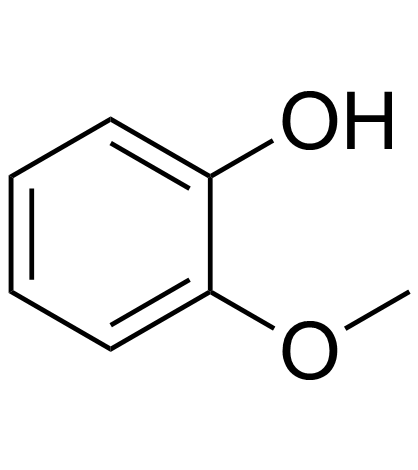 |
愈创木酚
CAS:90-05-1 |
|
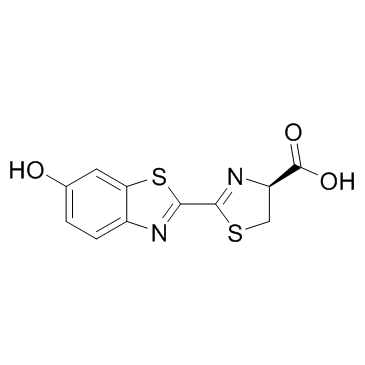 |
D-(-)-荧光素
CAS:2591-17-5 |
|
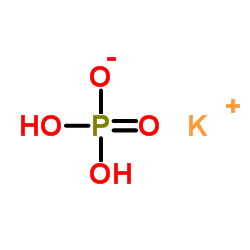 |
磷酸二氢钾
CAS:7778-77-0 |
|
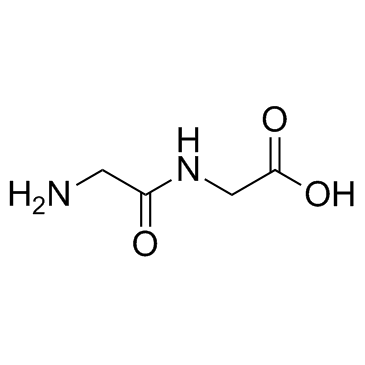 |
双甘肽
CAS:556-50-3 |
|
 |
他莫昔芬
CAS:10540-29-1 |
|
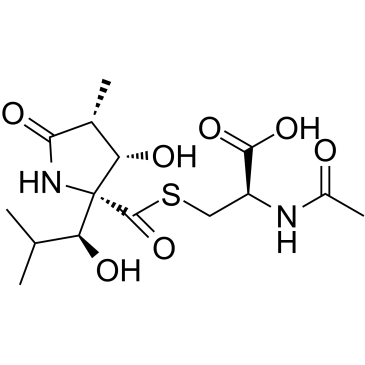 |
乳胞素
CAS:133343-34-7 |