| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
 |
氯化钠
CAS:7647-14-5 |
|
 |
十二烷基硫酸钠
CAS:151-21-3 |
|
 |
无水氯化钙
CAS:10043-52-4 |
|
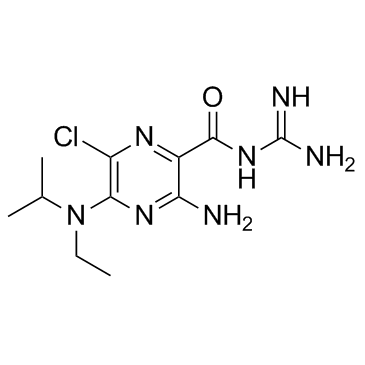 |
5-(N-乙基-N-异丙基)阿米洛利
CAS:1154-25-2 |
|
 |
D(+)-无水葡萄糖
CAS:50-99-7 |
|
 |
氯化钠-35cl
CAS:20510-55-8 |
|
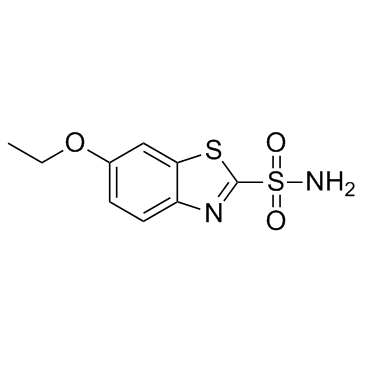 |
依索唑胺
CAS:452-35-7 |
|
 |
氯化镁
CAS:7786-30-3 |
|
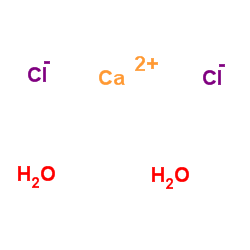 |
二水氯化钙
CAS:10035-04-8 |
|
 |
3-乙氧酰基苯胺甲磺酸盐
CAS:886-86-2 |