| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
 |
氯化钠
CAS:7647-14-5 |
|
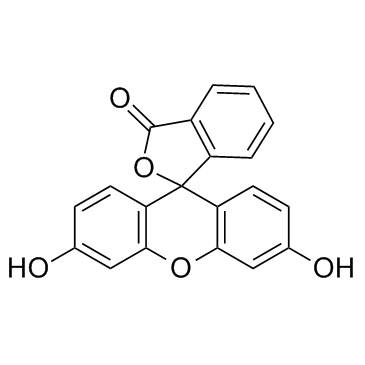 |
荧光素
CAS:2321-07-5 |
|
 |
氯化钠-35cl
CAS:20510-55-8 |
|
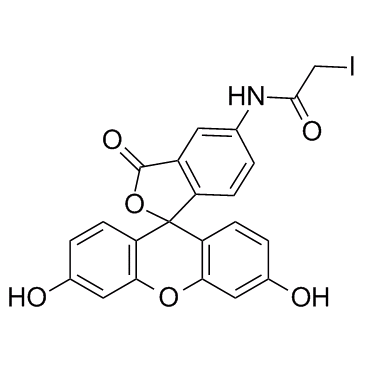 |
5-碘乙酰氨基荧光素
CAS:63368-54-7 |
|
 |
N,N-二异丙基乙胺
CAS:7087-68-5 |