| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
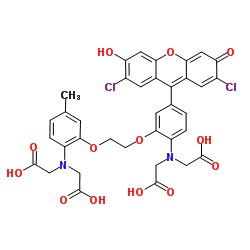 |
荧光钙探针FLUO-3
CAS:123632-39-3 |
|
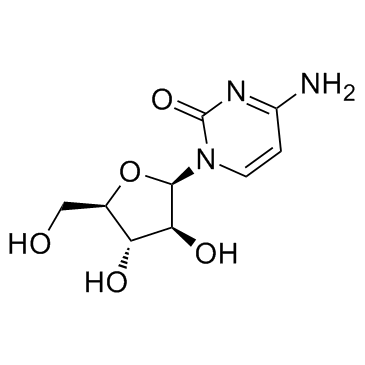 |
阿糖胞苷
CAS:147-94-4 |
|
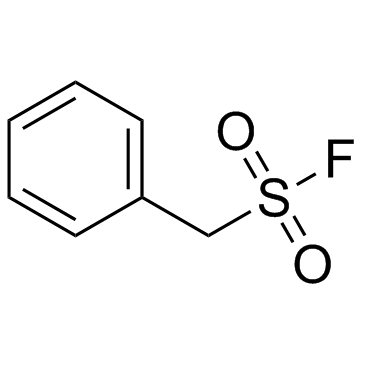 |
苄磺酰氟
CAS:329-98-6 |
|
 |
BAPTA-AM
CAS:126150-97-8 |
|
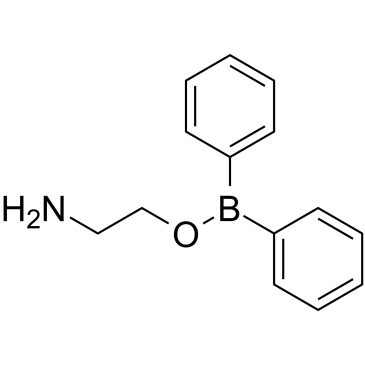 |
2-氨基乙基联苯基硼酸酯
CAS:524-95-8 |