| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
 |
溴化乙啶
CAS:1239-45-8 |
|
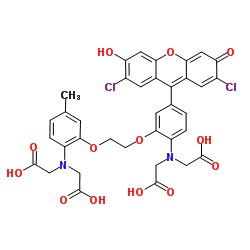 |
荧光钙探针FLUO-3
CAS:123632-39-3 |
|
 |
氯化钠
CAS:7647-14-5 |
|
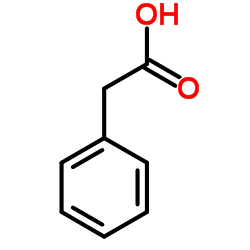 |
苯乙酸
CAS:103-82-2 |
|
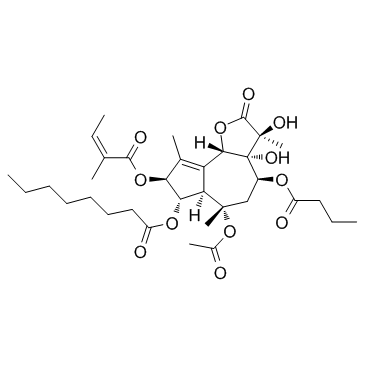 |
毒胡萝卜素
CAS:67526-95-8 |
|
 |
氯化钠-35cl
CAS:20510-55-8 |
|
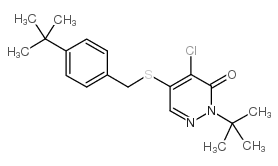 |
哒螨灵
CAS:96489-71-3 |
|
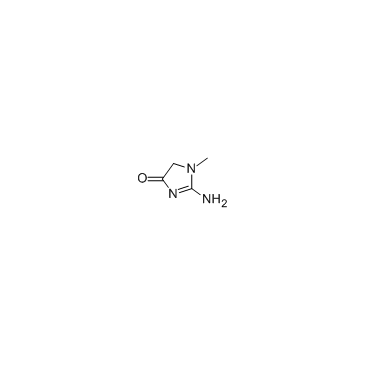 |
肌酐
CAS:60-27-5 |
|
 |
乙二胺四乙酸
CAS:60-00-4 |