| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
 |
丙酮
CAS:67-64-1 |
|
 |
S-亚硝基谷胱甘肽
CAS:57564-91-7 |
|
 |
抗坏血酸
CAS:50-81-7 |
|
 |
曲古柳菌素A
CAS:58880-19-6 |
|
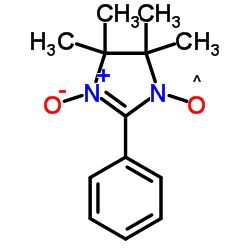 |
3-氧代-2-苯基-4,4,5,5-四甲基咪唑啉-1-氧
CAS:18390-00-6 |