| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
 |
硫酸
CAS:7664-93-9 |
|
 |
氢氧化钠
CAS:1310-73-2 |
|
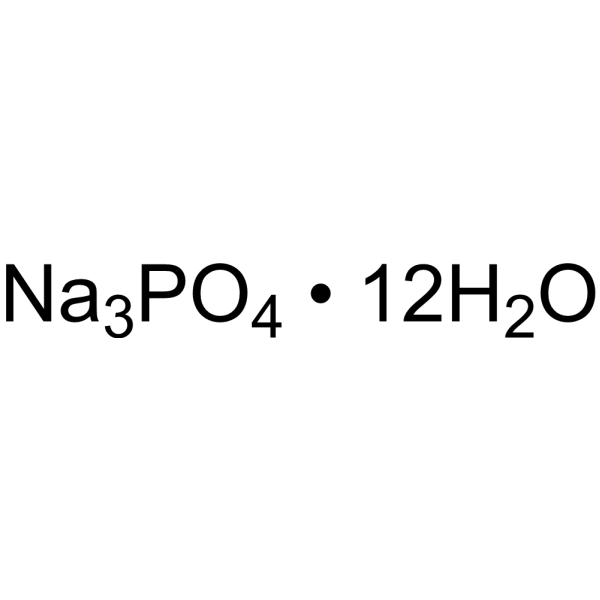 |
磷酸三钠,十二水合物
CAS:10101-89-0 |
|
 |
抗坏血酸
CAS:50-81-7 |
|
 |
3-乙基-2,4-戊烷二酮
CAS:1540-34-7 |
|
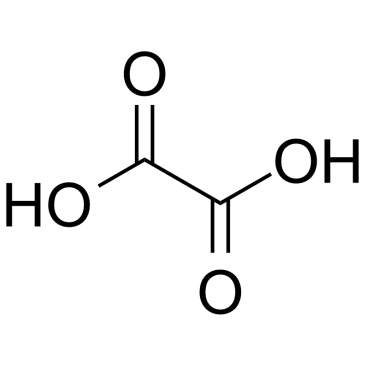 |
草酸
CAS:144-62-7 |
|
 |
纳米四氧化三铁
CAS:1317-61-9 |
|
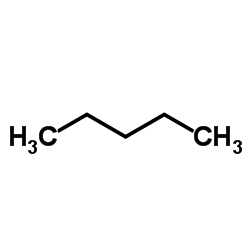 |
正戊烷
CAS:109-66-0 |
|
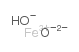 |
水合氧化铁(III)
CAS:20344-49-4 |